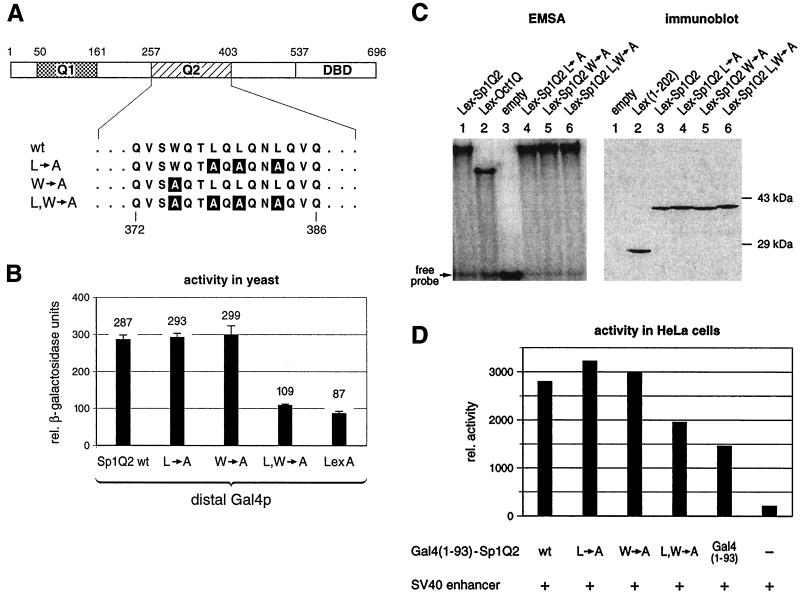
FIG. 5.
Mutations in Sp1Q2 similarly affect its activation potential in both yeast and human cells. (A) Substitutions of three leucines to alanines (L→A) and a tryptophan to an alanine (W→A), which are known to affect the interaction with dTAFII110 and gene activation in Drosophila cells, were introduced in the Q2 activation domain of Sp1. In addition, both types of mutations were combined (L, W→A), resulting in a four-amino-acid exchange in the 147-amino-acid-long activation domain. (B) Yeast strains containing the reporter gene as described in Fig. 2A were transformed with plasmids encoding the Gal4 activator and different Lex-Sp1Q2 mutants or wild type. Quantitative β-galactosidase assays showed that the two mutants (L→A and W→A) still activated gene expression as much as the wild type. Only the combination mutant (L, W→A) diminished the transactivation potential of the Q2 domain. (C) Mutant and wild-type Sp1Q2 fusion proteins bind similarly to the Lex binding sites. EMSAs were performed by using total protein extracts from yeast cells and 32P-labeled oligonucleotide duplex containing two Lex binding sites. Equal amounts of protein were used for each EMSA. The Sp1Q2 mutants (lanes 4 to 6) bound to the Lex binding sites as well as the wild type (lane 1), indicating similar protein expression levels. Protein extracts from isogenic yeast cells containing an empty expression plasmid did not yield any detectable bandshifts (lane 3). The immunoblot using anti-LexA antibodies showed similar expression of the wild-type Sp1Q2 and the different mutants. (D) Transfection of HeLa cells with wild-type and mutant Sp1Q2. The mutants tested in yeast were subcloned as Gal4 (amino acids 1 to 93) hybrids into a mammalian expression vector. These transactivator plasmids were cotransfected into HeLa cells along with a reporter plasmid, under the control of two proximal Gal4 binding sites and a downstream SV40 enhancer (see Fig. 1A), and a reference plasmid. S1 nuclease analysis was performed, and the signals were quantified by using a PhosphorImager. As in yeast (Fig. 4B), the mutants L→A and W→A had the same transactivation potential as wild-type Sp1Q2. Only the combined mutations L, W→A showed a reduced ability to stimulate reporter gene expression, which was still above background.