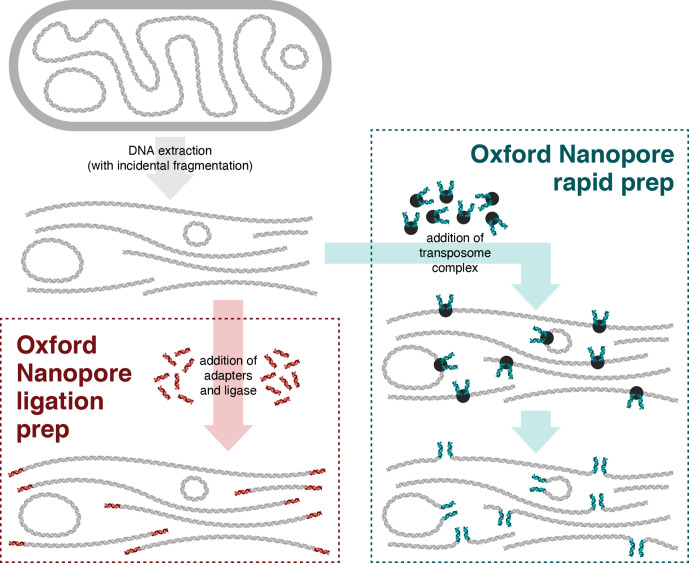
Fig. 1.
Conceptual illustration of Oxford Nanopore ligation and rapid sample preparation methods. When circular DNA is extracted from a bacterial cell (top-left), incidental fragmentation of the DNA occurs. The ligation preparation (bottom-left) comprises blunt-end ligation of barcodes/adapters onto DNA molecules, so circular pieces of DNA will not receive adapters and thus remain unavailable for sequencing. The rapid preparation (right) uses a transposome enzyme to add barcodes/adapters into the middle of DNA molecules, making both linear and circular DNA available for sequencing.