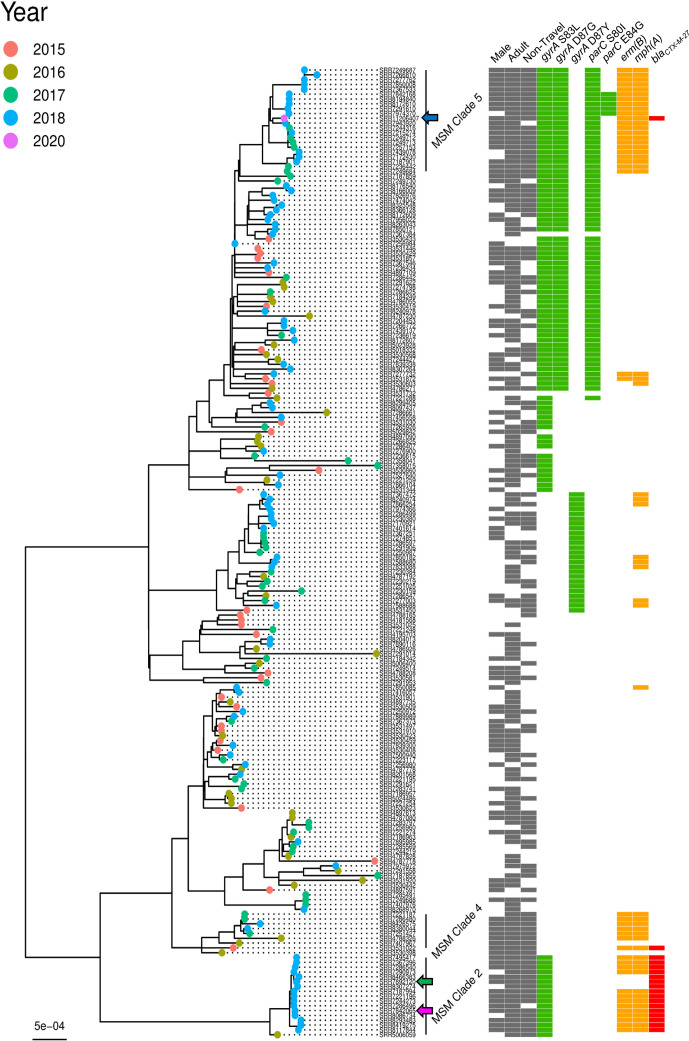
Fig. 4.
Maximum-likelihood phylogeny of three S. sonnei isolates known to be associated with men who have sex with men that were sequenced using Nanopore technologies in this study, compared to other isolates in Public Health England’s collections. To place the isolates in context, 198 other S. flexneri isolates that are representatives from relevant SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) clusters were included in the comparison. S. sonnei isolates investigated in detail in this study are as follows; 598 080 (SRR7842065, pink filled arrow), 607 387 (SRR7892120, green filled arrow), 893 916 (SRR11206407, blue filled arrow). Isolates are labelled by SRR number and tip nodes are coloured by year of receipt. S. sonnei MSM clades are labelled as per those described in Baker et al. [8]. Adjacent grey blocks in each of the first three columns (left-right) indicate the sample was isolated from a male, an adult, and that the illness was non-travel related (left-right). Grey blocks in these three lanes for an isolate implies the infection may be associated with MSM transmission. Presence of antimicrobial resistance genes concerning fluoroquinolones (mutations in gyrA and parC, green) and macrolides (erm(B) and mph(A), orange) are taken from Bardsley et al. [45] and presence of blaCTX-M-27 was determined using GeneFinder. Gene presence is indicated by a coloured tile in the relevant column. ML trees are midpoint rooted and scale bar indicates SNPs.