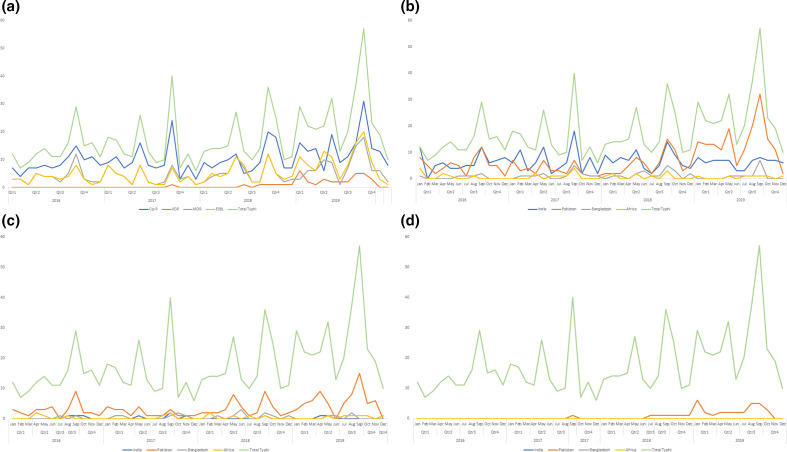
Fig. 4.
Trends of ciprofloxacin resistance in S. Typhi associated with travel to India, Pakistan, Bangladesh and Africa with y-axis showing the number of isolates. (a, b) Trends of resistance in S. Typhi cases received between 2016 and 2019 based on the presence of AMR determinant markers and subdivided into four main categories (Cip R, ciprofloxacin-resistant strains; ESBL, extended spectrum β-lactamase producing strains; MDR, multidrug resistant strains; XDR, extensively drug resistant strains) (a) and trends of ciprofloxacin resistance in S. Typhi associated with travel to India, Pakistan, Bangladesh and Africa (b). (c, d) Trends of MDR (c) and XDR (d) S. Typhi associated with travel to India, Pakistan, Bangladesh and Africa. Figures show an increase of S. Typhi Cip R, ESBL, MDR and XDR strains over time, with the largest increase in 2019 and with travel to Pakistan.