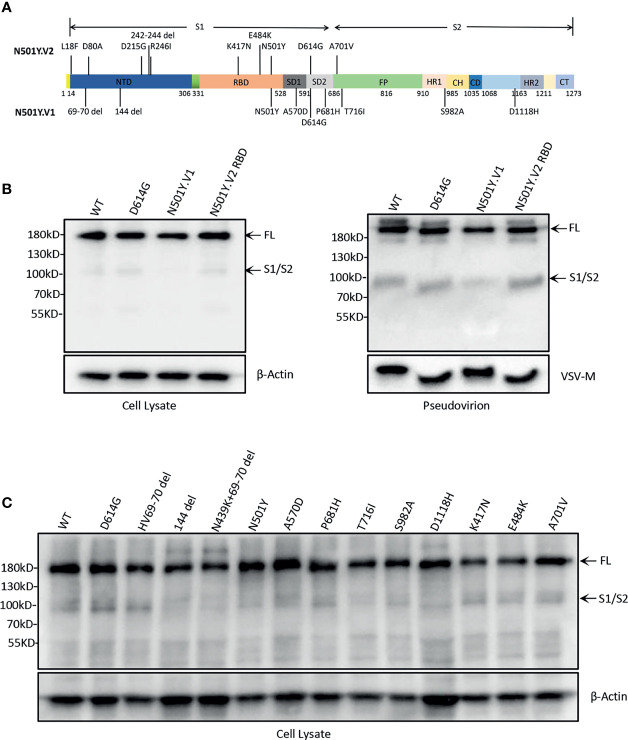
Figure 1.
SARS-CoV-2 variants spike protein expression and incorporation into pseudovirions. (A) Construction of SARS-CoV-2 variants N501Y.V1, N501Y.V2, and N501Y.V2 RBD S protein. The S protein of N501Y.V1 include nine mutations (HV69-70 del, 144 del, N501Y, D614G, P681H, T716I, S982A, and D1118H), N501Y.V2 include ten mutations (L18F, D80A, D215G, 242-244 del, R246I, K417N, E484K, N501Y, D614G and A701V) and N501Y-V2 RBD include D614G and three major mutations in the RBD (K417N, E484K and N501Y). (B) Analysis of S protein expression and particle incorporation of N501Y.V1 and N501Y.V2 RBD lineages. The S proteins expression and incorporation to pseudovirion were measured by western blot using antibody against spike. β-Actin (cell lysates) and VSV-M (particles) served as loading controls. Full-length S protein and S1/S2 cleavage are annotated. Shown are representative blots from three experiments. (C) Analysis of the S protein expression of single-site mutation of spike protein in N501Y.V1 and N501Y.V2 lineages by western blot. The S proteins expression were detected in cell lysate by western blot using antibody against S protein, and β-Actin served as loading controls.