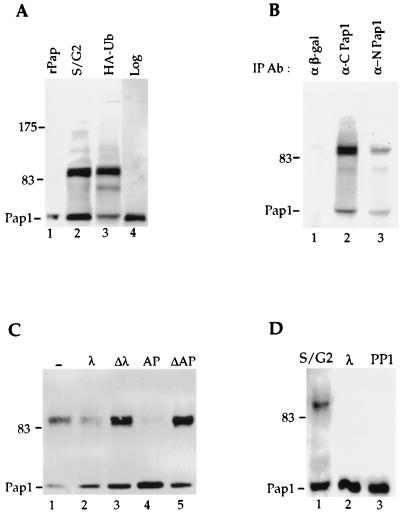
FIG. 3.
Pap1 phosphorylation. (A) Pap1 was immunoprecipitated from extract prepared from synchronized Fc12-18 cells which have entered late S/G2 after release from α-factor arrest (lane 2), from unsynchronized W303 cells overexpressing HA-ubiquitin (lane 3), or from unsynchronized W303 cells without ubiquitin overexpression (lane 4). rPap is recombinant Pap1 made in E. coli (lane 1). (B) Extracts from W303 cells overexpressing ubiquitin were immunoprecipitated with anti-β-galactosidase (α β-gal) (lane 1) or with the C-terminal (lane 2) or N-terminal (lane 3) Pap1 antibodies, and the immunoblot was probed with the C-terminal Pap1 antibody. IP Ab, immunoprecipitation antibody. (C) The 90-kDa Pap1 species is sensitive to phosphatases. Immunoprecipitates were incubated without phosphatase (−) (lane 1) or with 200 U of lambda phosphatase (λ) (lane 2), 2 U of alkaline phosphatase (AP) (lane 4), or heat-inactivated lambda phosphatase (Δλ) (lane 3) on alkaline phosphatase (ΔAP) (lane 5). (D) Phosphorylation of Pap1 at S/G2 of the cell cycle. Phosphatase treatment of the Pap1 immunoprecipitate from the 90-min time point shown in Fig. 1B. Lane 1, no phosphatase; lane 2, lambda phosphatase; lane 3, protein phosphatase 1 (PP1). Unless indicated otherwise, the immunoprecipitations and immunoblotting were performed with the C-terminus-specific Pap antibody. The positions of molecular mass markers (in kilodaltons) are indicated to the left of the gels.