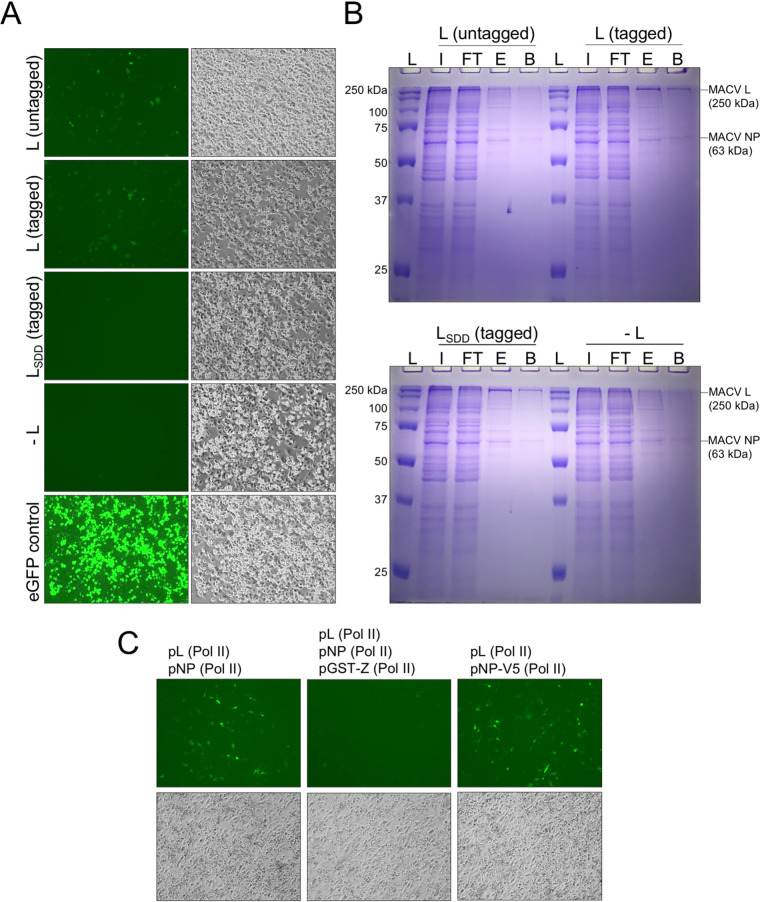
FIG 3.
Further characterization of affinity-tagged L and NP in the MACV RNP system. (A) Comparison of minireplicon replication and gene expression mediated by affinity-tagged MACV L in BSR-T7 cells. Bright-field images of infected and transfected cells are shown in the left-hand column. Fluorescence microscopy images of the eGFP-expressing cells in the same field of view are shown in the right-hand column. Cells were transfected with the minireplicon RNA (pMG) and nucleoprotein-expressing (pNP) plasmids, in combination with either wild-type L (untagged), L with C-terminal Flag and 6×His tags (tagged), catalytically inactive L with C-terminal tags (LSDD; tagged), or without any L-expressing plasmid (−L). Cells transfected with a plasmid encoding T7 RNAP-driven eGFP expression are shown in the bottom panel. (B) Ni-NTA purification of MACV L from RNP-expressing cells. Cells in panel B were collected and subjected to metal ion affinity purification as described in Materials and Methods. The sample fractions for each condition include the total cell lysate input (I), unbound flowthrough (FT), eluted sample (E) in 0.25 M imidazole, and residual bound proteins from the boiled Ni-NTA beads (B). Lane L contains the protein molecular weight ladder. (C) Further characterization of the modified RNP system with Pol II-expressed L and NP with introduced affinity tags. All cells in panels A and B were infected with T7-expressing vaccinia virus for expression of the minireplicon RNA prior to plasmid transfection.