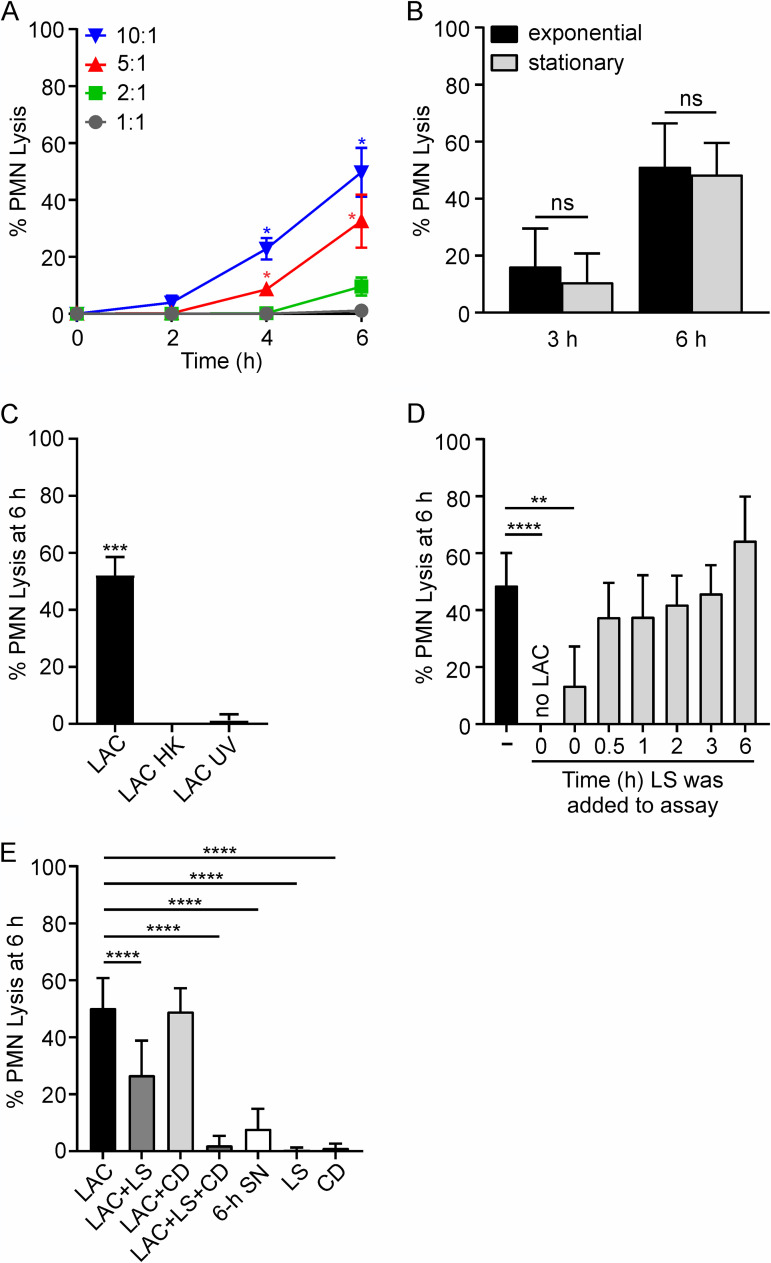
FIG 1.
Human PMN lysis after phagocytosis of USA300 strain LAC. (A) PMN lysis is dependent on time and bacterial cell-to-PMN ratio (n = 4). (B) PMN lysis is not influenced by bacterial growth phase (n ≥ 4). (C) PMN lysis after phagocytosis requires live S. aureus. Bacteria were heat killed (LAC HK) at 95°C for 5 min or UV irradiated (LAC UV) at 4,000 × 100 μJ/cm2 (n = 3). (D) Phagocytosed S. aureus are protected from killing by lysostaphin (LS). LS (6.5 U/107 CFU) was added to assays at the times indicated, and USA300-mediated PMN lysis was determined as described in Materials and Methods. (E) PMN lysis can be caused by intracellular and/or extracellular staphylococci. Cytochalasin D (CD; 10 μg/ml) was added to PMNs 15 min prior to addition of bacteria. LS was added 30 min after the start of the experiment when added alone (LAC+LS) or 15 min prior to addition of bacteria when added concurrently with CD (LAC+LS+CD) (n ≥ 3). To generate culture supernatant (SN), overnight cultures of LAC were diluted 1:100 into prewarmed RPMI/H and grown for 6 h at 37°C as described in Materials and Methods. Data are presented as mean values ± standard deviations (SD), and assays whose results are shown in panels B to E were performed using a 10:1 bacterial cell/PMN ratio. (A) Data were analyzed using repeated-measures ANOVA and Tukey’s posttest. Asterisks marking data colored blue and red indicate a P value of <0.05 versus all other bacterial cell/PMN ratios at 4 h and versus 1:1 and 2:1 ratios at 6 h. (B) Results were analyzed using an unpaired two-tailed t test. ns, not significant. (C, D) Data were analyzed using repeated-measures ANOVA and Tukey’s posttest. **, P < 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001; ****, P ≤ 0.0001. (E) Data were analyzed with mixed-effects analysis and Dunnett’s posttest. ****, P ≤ 0.0001.