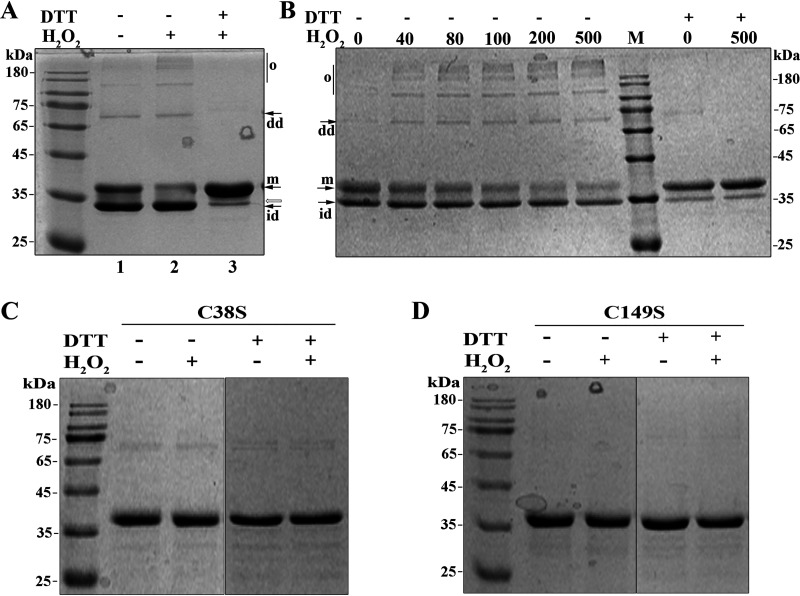
FIG 2.
Nonreducing SDS-PAGE examines H2O2 oxidation-caused Cys38-Cys149 disulfide linkages in So-RNaseZ. (A) The recombinant So-RNaseZ was treated with or without 500 μM H2O2 for 30 min and subsequently reduced with 10 mM DTT. (B) The recombinant So-RNaseZ was treated with a gradient of concentrations of H2O2 (μM) for 30 min and subsequently reduced with 10 mM DTT. M, molecular weight marker; m, So-RNaseZ monomer; id, intramolecular disulfide linkage; dd, disulfide-linked dimer; and o, disulfide-linked oligomers. Empty arrow indicates the band containing a presumed different conformation of So-RNaseZ monomer as identified by MALDI-TOF (Fig. S3). (C and D) Cys38 and Cys149 of So-RNaseZ were each mutated into serine and mutant proteins were overexpressed in E. coli. Purified So-RNaseZC38S (C38S) (C) and So-RNaseZC149S (C149S) (D) were treated with or without 500 μM H2O2 for 30 min and subsequently reduced using 10 mM DTT. The statuses of wild-type and cysteine-mutated So-RNaseZ proteins were examined by 12% nonreducing SDS-PAGE. Molecular weight marker is shown beside the gel. Experiments were repeated at least three times, and representative results are shown.