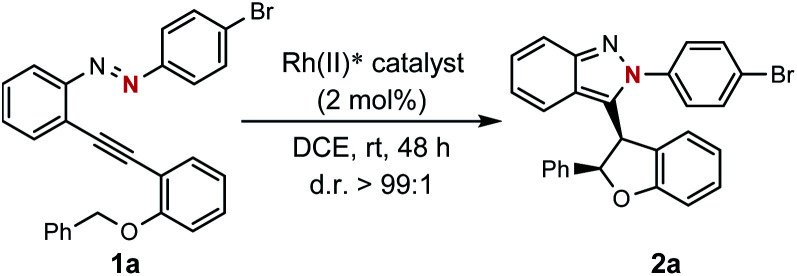
Optimization of reaction conditionsa.
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Rh(ii)* | Solvent | Yieldb [%] | erc |
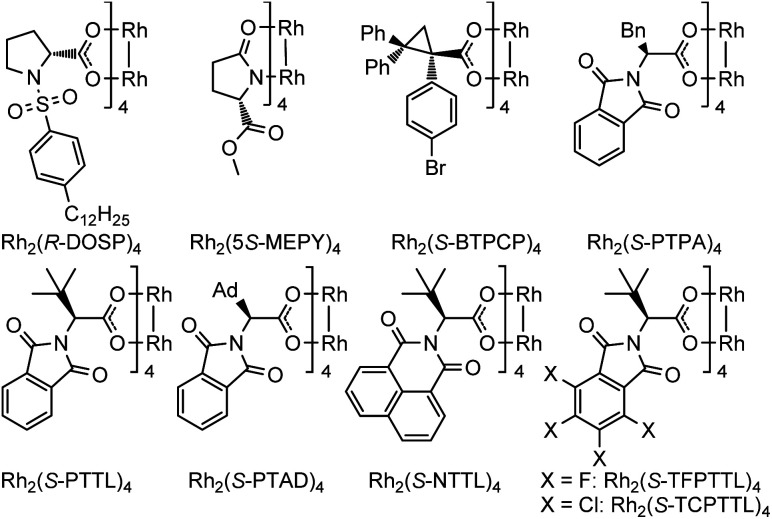
| 1 | Rh2(R-DOSP)4 | DCE | 56 | 29 : 71 |
| 2 | Rh2(5S-MEPY)4 | DCE | 17 | 50 : 50 |
| 3 | Rh2(S-BTPCP)4 | DCE | 61 | 8 : 92 |
| 4 | Rh2(S-PTPA)4 | DCE | 91 | 91 : 9 |
| 5 | Rh2(S-PTTL)4 | DCE | 86 | 97 : 3 |
| 6 | Rh2(S-PTAD)4 | DCE | 93 | 94 : 6 |
| 7 | Rh2(S-NTTL)4 | DCE | 92 | 96 : 4 |
| 8 | Rh2(S-TCPTTL)4 | DCE | 95 | 98 : 2 |
| 9 | Rh 2 (S-TFPTTL) 4 | DCE | 98 d | 98 : 2 |
| 10 | Rh2(S-TFPTTL)4 | DCM | 88 | 98 : 2 |
| 11 | Rh2(S-TFPTTL)4 | Toluene | 92 | 98 : 2 |
| 12 | Rh2(S-TFPTTL)4 | MeCN | 16 | 92 : 8 |
| 13 | Rh2(S-TFPTTL)4 | n-Hexane | 96 | 98 : 2 |
| 14e | Rh2(S-TFPTTL)4 | DCE | 65f | 96 : 4 |
| ||||
Unless otherwise noted, reactions were performed at 0.1 M in DCE using 0.20 mmol substrate and catalyst (2 mol%) under a N2 atmosphere.
Determined by 1H NMR spectroscopy.
The er value of 2a was determined by HPLC using a chiral stationary phase.
Isolated yields.
1 mol% catalyst was used.
25% starting material was recovered.
