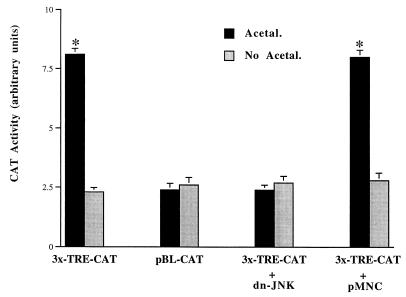
FIG. 5.
Acetaldehyde induces AP-1 activation via a JNK-dependent pathway. Sixty- to eighty-percent confluent HSC were transfected with either an AP-1 reporter plasmid, 3x-TRE-CAT, or an empty control plasmid, pBL-CAT. The AP-1 reporter plasmid 3x-TRE-CAT contains three AP-1 binding sites upstream of a CAT reporter gene. In cotransfection experiments, HSC were cotransfected with 3x-TRE-CAT and a dominant-negative JNK expression plasmid (dn-JNK) or an empty control plasmid, pMNC. After recovery, the transfected cells were treated with or without acetaldehyde (100 μM) for an additional 36 h in DMEM containing 0.4% fetal bovine serum. Transfection efficiency was normalized by measurement of β-galactosidase activity (see Materials and Methods). Values are expressed as means ± standard deviations (n = 6). ∗, P < 0.05 compared with the control (No Acetal).