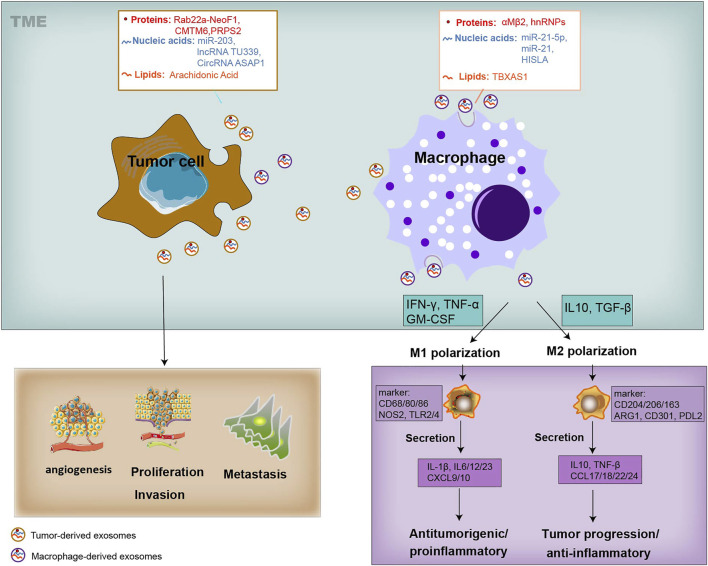
FIGURE 1.
Systematic representation of the exosome-mediated crosstalk between TAMs and tumor within the TME. Exosomes can be released by TAMs and tumor cells, and transfer information to the recipient cells. Exosomes derived from TAMs can transfer their cargo proteins (αMβ2, hnRNPs), nucleic acids (miR-21-5p, miR-21 and HISLA), and lipids (TBXAS1) to TME by tumor cells, affecting tumor biology, including cell proliferation, angiogenesis, metastasis, and T-cell cytotoxic activity. Tumor cells-derived exosomes cargo proteins (Rab22a-NeoF1, CMTM6, PRPS2), nucleic acids (miR-203, TU339 and circASAP1), and lipids (AA), and educate the polarization and differentiation of macrophages into the cancer-inhibiting M1 (proinflammatory) and cancer-promoting M2 phenotype (anti-inflammatory). The activation of M1 type macrophages occurs through signal transduction of IFN-γ, TNF and Toll-like receptors (TLR). M1 cells produce nitric oxide (NO), reactive oxygen species (ROS) and pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, IL-12, IL-23, CXCL9, CXCL10, TNF-α, and MHC molecules. Genetic markers related to M1 polarization include IL1a, IL1b, IL6, NOS2, TLR2, TLR4, CD80 and CD86. The activation of M2 macrophages is mediated by various cytokines. M2 cells tend to express an immune suppressive phenotype, and produce anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-10, TGF-β, CCL17, CCL18, CCL22, and CCL24. Surface proteins include CD115, CD206, PPARG, ARG1, CD163, CD301, Dectin-1, PDL2 and Fizz1.