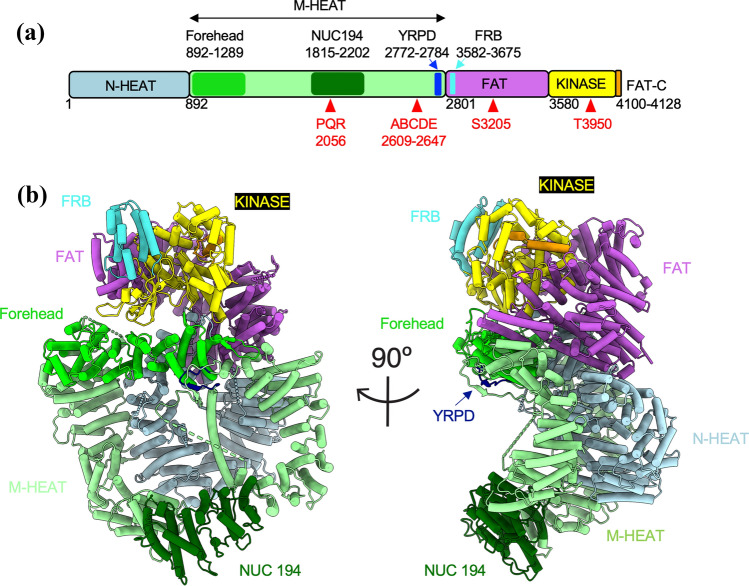
Fig. 1.
Structure of DNA-PKcs. A Schematic of DNA-PKcs showing the N-HEAT domain (residues 1–891, light blue), the M-HEAT domain (residues 892–2800, light green), the FAT domain (residues 2801–3579, purple), the kinase domain (3580–4099, yellow) and the FATC domain (4100–4128, orange). Also shown is the position of the conserved forehead domain (892–1289, bright green) and the NUC194 domain (residues 1815–2202, dark green), the YRPD motif (residues 2772–2784, dark blue), the FRB domain (residues 3582–3675, bright blue) and the positions of the PQR, ABCDE, S3205 and T3950 phosphorylation sites (red triangles). B Two views of DNA-PKcs (from PDB 7LT3) (Chen et al., 2021a), rotated by 90°, colored as in A. The YRPD motif is shown in dark blue, most clearly visible in the side view, indicated by an arrow. See Lees-Miller et al., (2020) for conservation of amino acids in the forehead and NUC194 domains in DNA-PKcs from eukaryotes