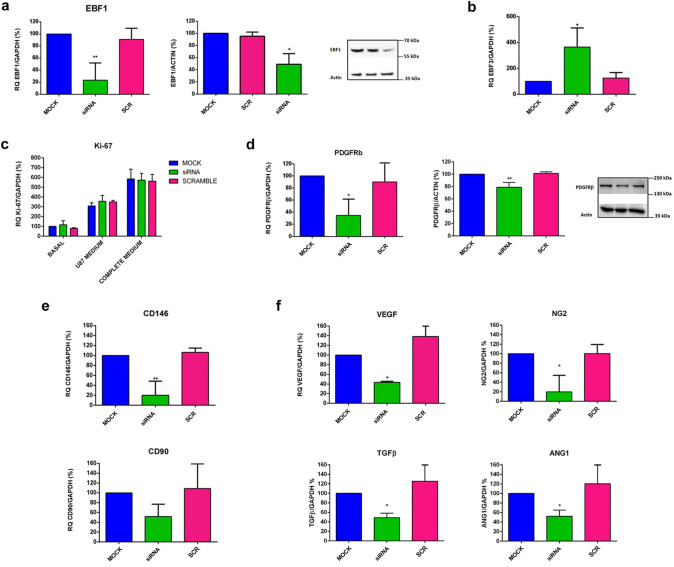
Fig. 6.
EBF1 plays a key role in the pericyte phenotype cell commitment. a Significant downregulation of EBF1 mRNA levels (about 75% decrease; p < 0.01) was obtained in HBVPs by means of siRNA technology, measured by RT-qPCR 24 h after transfection (upper histogram). Immunoblotting performed with protein extracts confirmed the reduction in the synthesis of EBF1 protein (about 50% decrease; p < 0.05). The representative image on the right shows the corresponding EBF1 band at 66 kDa. b Histogram shows that after EBF1 silencing, the expression of EBF3, a marker linked to the MSC phenotype, is significantly increased (p < 0.05). c Silencing of EBF1 does not affect cell proliferation as assessed by the evaluation of the nuclear antigen Ki-67 expression by RT-qPCR, 24 h after seeding cells with or without the addition of different proliferative stimuli, such as the medium from U87 glioblastoma cells cultured under hypoxic conditions or the complete culture medium containing PGS and 10% FBS. d We then investigated whether EBF1 silencing affects the phenotype of the pericytes. Indeed, the histograms show a significant reduction in the main pericyte markers PDGFRβ (p < 0.05) at both the transcriptional (p < 0.05) and protein (p < 0.01) levels. e Additionally, we found a significant reduction in the pericyte marker CD146 (p < 0.01). The expression levels of CD90, a marker linked to a mesenchymal phenotype, did not show a significant reduction. f Of note, the expression levels of VEGF, Ang-1, NG2 and TGF-β, cytokines produced by pericytes during different phases of angiogenesis are significantly reduced in EBF1-silenced HBVPs (p < 0.05). Overall, data confirmed a functional role of EBF1 in pericyte cell fate commitment and functionality. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. CTRL (control); siRNA (EBF1-silenced); SCR (scramble, control siRNA); Basal (basal conditions); Hypoxic (hypoxic conditions)