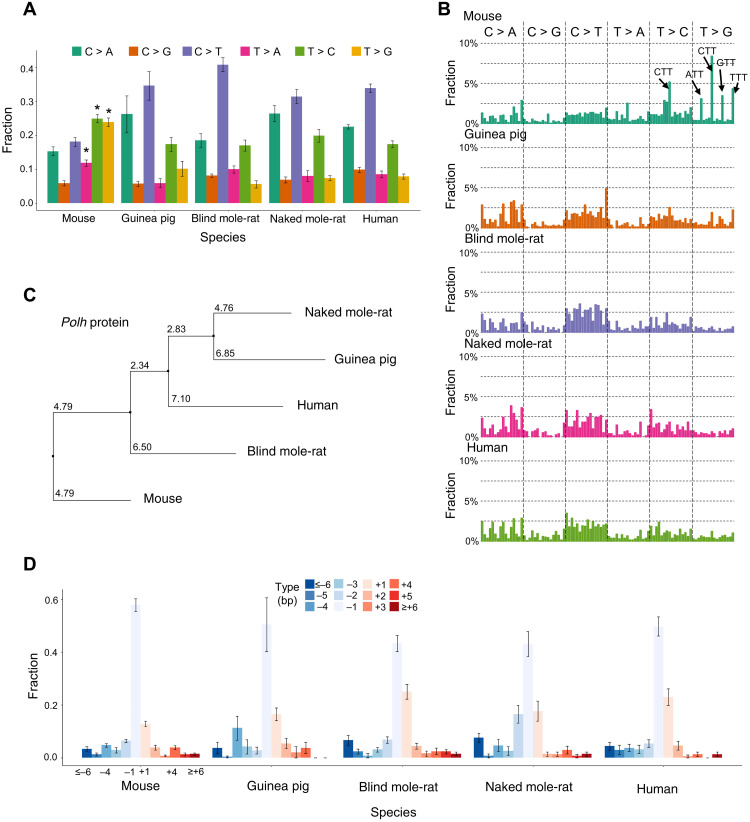
Fig. 2. Mutational spectra of spontaneous somatic mutations.
(A) Mutational spectra of spontaneous somatic SNVs. (B) Mutational spectra of spontaneous somatic SNVs in the context of their two flanking base pairs. This classified mutations into 96 categories. On the x axis, the 96 categories were sorted according to their alphabetic order. For example, the first bar from the left indicates ACA to AAA mutation, and the first from the right indicates TTT to TGT mutation. The y axis indicates the fraction of each category out of the total number of mutations. (C) A phylogeny tree of protein sequences of the Polh orthologs of the five species. Multiple sequence alignment was performed using Clustal Omega, and the phylogeny tree was calculated using the neighbor joining algorithm using Jalview based on the PID (i.e., the percentage identity between the two sequences at each aligned position) score, which indicates the number of identical residues per 100 residues. (D) Mutational spectra of spontaneous somatic INDELs. Error bars in (A) and (D) indicate SD.