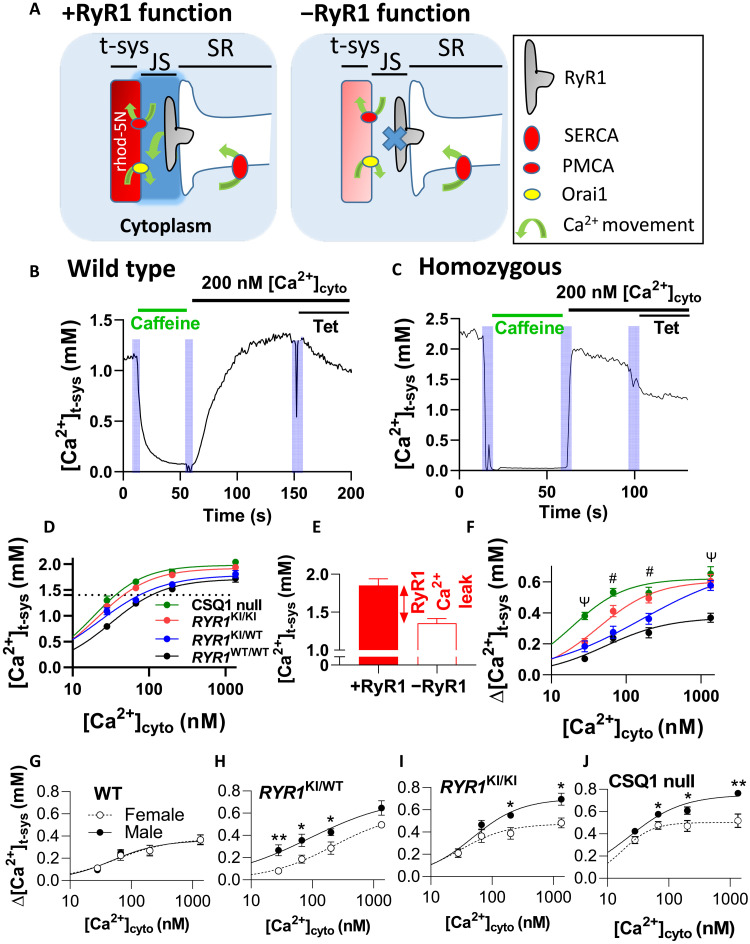
Fig. 1. RyR1 Ca2+ leak increases with RYR1 mutations and absence of CSQ1.
(A) Schematic depicting the detection of RyR1 Ca2+ leak using rhod-5N trapped in the sealed t-system. The presence of functional RyR1 (+RyR1) allows Ca2+ to leak into the JS and increase [Ca2+]JS above that of the bulk cytoplasm. [Ca2+]JS directly influences PMCA activity and [Ca2+]t-sys. When RyR1 leak is blocked with Tet (−RyR1), [Ca2+]t-sys drops. (B) [Ca2+]t-sys (t) in a WT fiber and (C) in an HOM fiber during SOCE activation in caffeine, followed by caffeine washout and addition of standard solution with 200 nM [Ca2+]cyto in the absence, then presence, of Tet. (D) Steady-state [Ca2+]t-sys versus [Ca2+]cyto in all genotypes. Intersection of dotted line and curves fitted to [Ca2+]t-sys indicates the [Ca2+]cyto where physiological [Ca2+]t-sys is reached. (E) Example of the determination of Δ[Ca2+]t-sys in +RyR1 and −RyR1 conditions in the presence of 200 nM [Ca2+]cyto (HOM fiber). The difference between the histograms (Δ[Ca2+]t-sys) is RyR1 Ca2+ leak (text on panel). (F) RyR1 Ca2+ leak in each genotype. (G to J) RyR1 Ca2+ leak in genotypes by sex. Data are presented as means ± SEM and fitted by Hill curves. Statistics and n value details are in Materials and Methods. Two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) [in (F)]: # = 4 significant results and Ψ = 3 significant results. Unpaired t test [in (G to J)]: *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01. The N [in (D) and (F)] had a sex ratio of 1, and n [in (D) and (F)] had a sex ratio close to 1. In (G) to (J), N = 6 to 8 mice per genotype, n = 11 to 20 fibers per point with a sex ratio of approximately 1 for each.