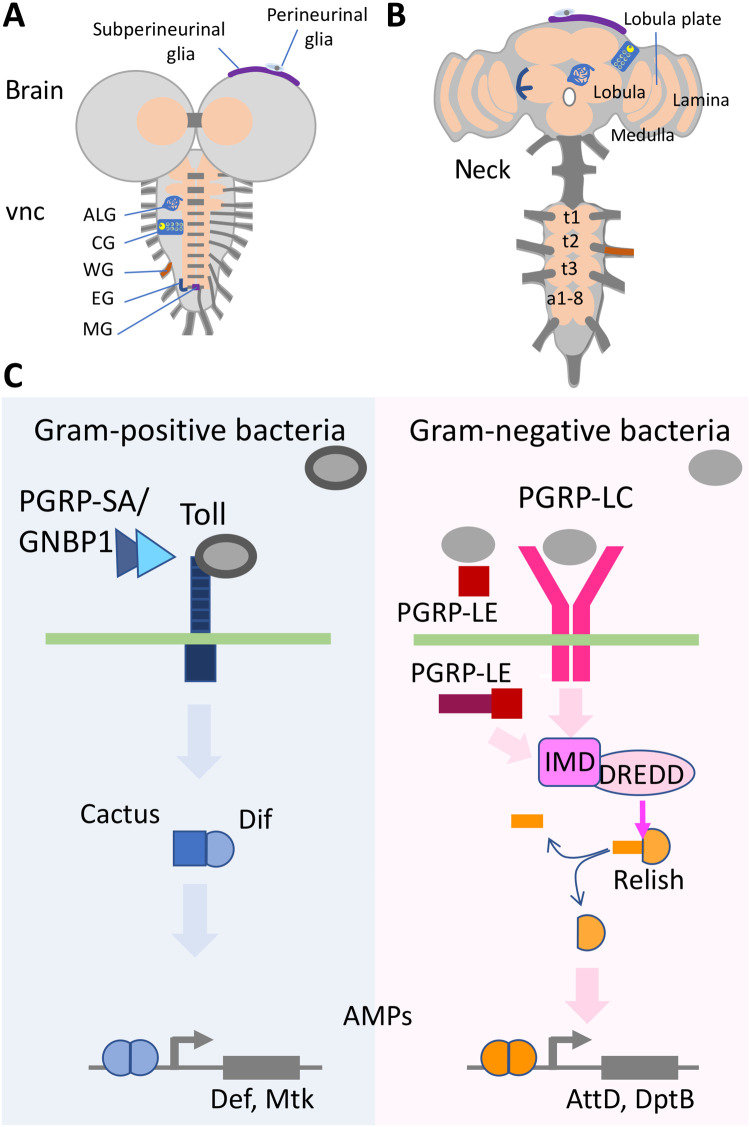
Fig. 1. Drosophila brains and immunity induction.
(A and B) Schematic view of (A) a third instar larval CNS and (B) an adult brain each composed of the ventral nerve cord (vnc) and the brain lobes. The subperineurial and the perineurial glia establish the BBB. The remaining glial cell types are astrocyte-like glia (ALG), cortex glia (CG), wrapping glia (WG), ensheathing glia (EG), and midline glia (MG). The thoracic neuromeres (t1 to t3) expand during pupal development, while the abdominal neuromers a1-8 condense. Some neuropil areas of the adult are indicated. (C) Signaling pathways directing the innate immune response. The Toll pathway is preferentially activated by Gram-positive bacteria, and the peptidoglycan recognition proteins (PGRP-LC and PGRP-LE) detect mostly Gram-negative bacteria. All relevant components are indicated. For further details, see main text.