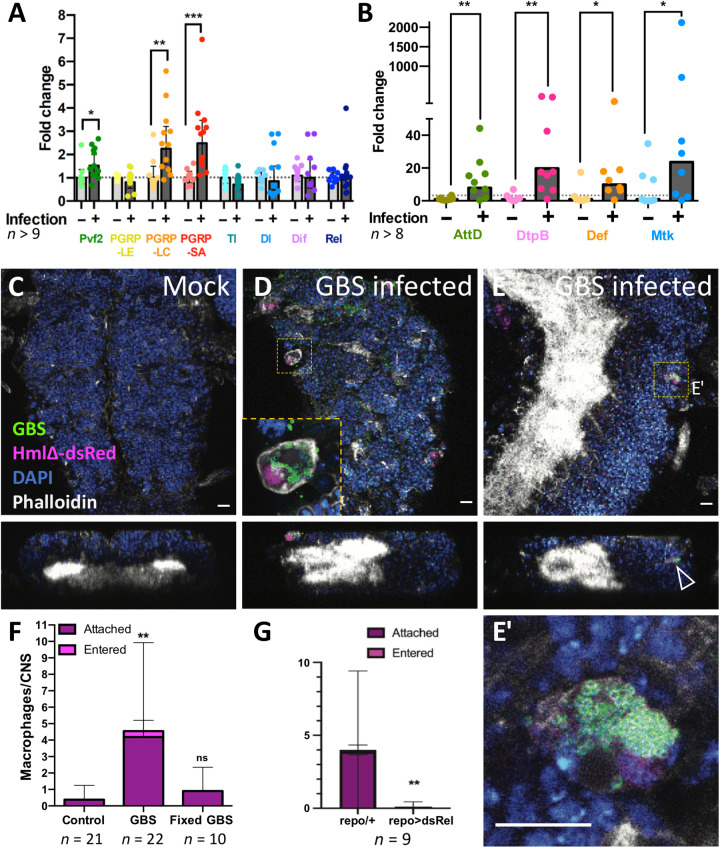
Fig. 10. GBS infection leads to immunity induction and macrophage recruitment in early pupal brains.
(A and B) Wandering third instar Drosophila larvae injected with GBS were dissected 4 to 5 hours after infection, and the brains were subjected to qPCR. Expression of the genes PGRP-LC, PGRP-SA, Pvf2, and all AMPs tested (AttD, DtpB, Def, and Mtk) was up-regulated upon infection. Mann-Whitney test for Pvf2, *P = 0.0227; PGRP-LC, **P = 0.0024; PGRP-SA, ***P = 0.0002; AttD, **P = 0.0055; DtpB, **P = 0.0025; Def, *P = 0.0207; Mtk, *P = 0.0499. Unpaired t test for PGRP-LE, P = 0.5297; Tl, P = 0.0988; Dl, P = 0.6202; Dif, P = 0.6758. (C to E) Macrophage recruitment and infiltration to GBS-infected pupal brains. Confocal images (top and orthogonal views) showing Drosophila CNS of hml-dsRed pupae 4 to 5 hours after injection in the hemolymph of either (C) Mock or (D and E) GBS. Macrophages (hml-dsRed in magenta) containing GBS (anti-GBS in green) are detected attached to the CNS (D, inset) or inside the CNS (E). (E′) is a close-up of the dotted boxes from (E). The arrowhead points to a macrophage within the CNS cortex. Phalloidin is in white, and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) is in blue. Scale bars, 10 μm. (F) Quantification of macrophage localization in the whole CNS 4 to 5 hours after injection in the hemolymph of mock (control), GBS, or formaldehyde-fixed GBS. Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons test on brain-associated (attached + entered) macrophages was performed generating adjusted P values: **P(control vs. GBS) = 0.0011 and P(control vs. fixed-GBS) = 0.7165. Control, n = 21 CNS; GBS, n = 22 CNS; fixed-GBS, n = 10 CNS. (G) Number of srpHemo-moe::3xmCherry–expressing macrophages that attach to the brain upon GBS infection of repo-Gal4 animals and repo-Gal4>UAS-relishdsRNA animals [n = 9; **P = 0.0078, Mann-Whitney on brain-associated (attached + entered) macrophages].