FIG 3.
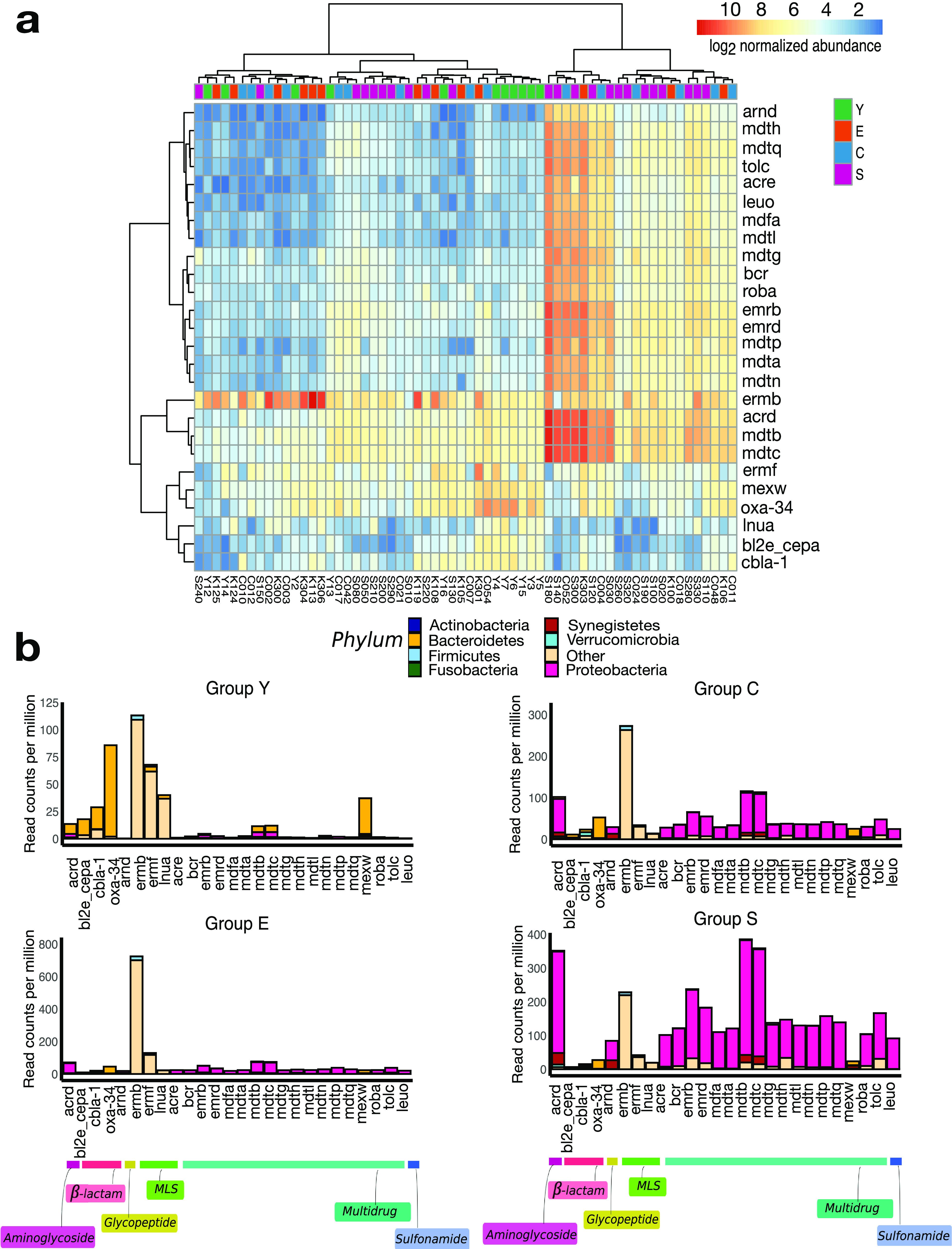
Age group-specific antibiotic resistance determinants. (a) Heat map computed on the abundances of counts normalized by library size and log2 scaled. The color code ranges from blue (low abundance) to red (high abundance). The samples are in columns, while the rows show the gene names of the antibiotic resistance determinants (ARDs) significantly associated with age, as identified by the three methods used (DESeq2, overdispersed Poisson generalized linear model, and Poisson regression model; Bonferroni corrected P value ≤ 0.05). Clustering was computed over Euclidean distances by the Ward linkage method. (b) Bar plots showing the normalized abundance (read counts per million normalized by sequencing depth) of age group-specific ARDs in the gut resistomes of young adults (group Y), younger elderly individuals (E), centenarians (C), and semisupercentenarians (S). Phylum-level assignments of ARD reads are also shown. ARDs are organized by drug to which resistance is conferred.
