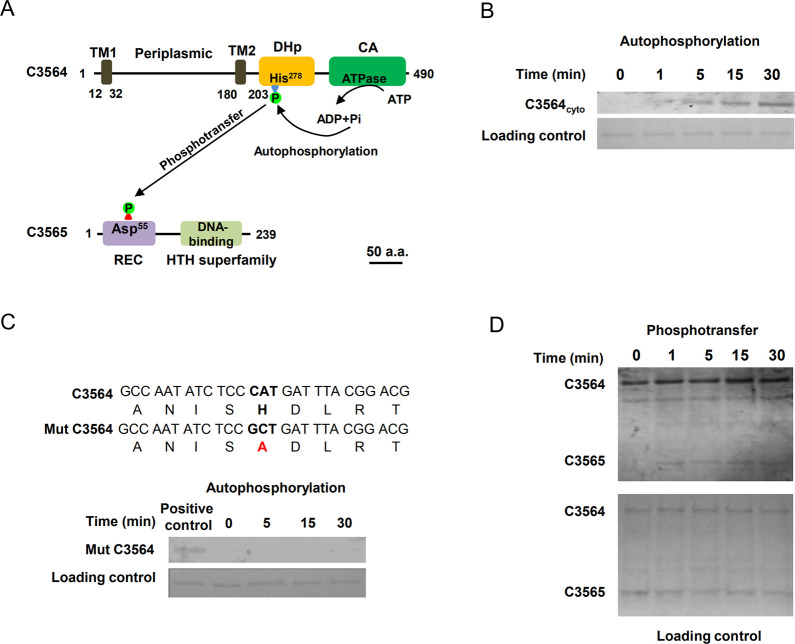
Fig 1. Identification of a two-component signaling system, C3564/C3565, in UPEC CFT073.
(A) Domain architectures of C3564 and C3565. The numbers indicate the amino acid positions. The domains were predicted with the InterPro database. Abbreviations: TM1 and TM2, two transmembrane helices; DHp, dimerization and histidine phosphorylation domain containing His278 for autophosphorylation; CA, catalytic ATPase domain; REC, receiver domain containing the putative aspartate residue for receiving the phosphoryl group; HTH, helix-turn-helix domain for DNA binding. The scale bar indicates 50 amino acids (a.a.). (B) In vitro analysis of C3564 autophosphorylation. The purified cytoplasmic portion of C3564 was incubated with ATP for various amounts of time, and phosphorylated proteins were detected using the pIMAGO-biotin phosphoprotein detection method. (C) Mutation of His278 abolished C3564 self-phosphorylation. Mut C3564 is a variant of C3564 carrying a His278Ala mutation, and the positive control is the wild-type C3564 protein. (D) In vitro transphosphorylation of C3565 by phosphorylated C3564. The autophosphorylated form of C3564 and purified C3565 protein were mixed at equimolar concentrations and then incubated at 37°C for the indicated amounts of time. The reaction mixture was directly subjected to SDS-PAGE and detected by the pIMAGO-biotin phosphoprotein detection method. These experiments were repeated at least twice, and representative images are shown.