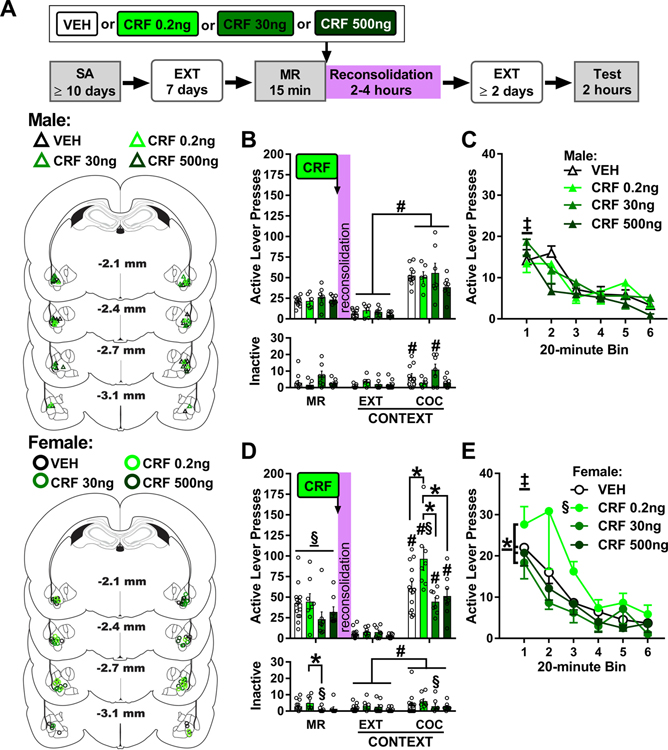
Figure 4. Intra-BLA CRF treatment immediately after memory reactivation dose-dependently increases drug context-induced cocaine seeking in female, but not male, rats three days later.
A) Experimental timeline. Rats were trained to self-administer cocaine (SA) in a distinct context, and their lever responding was then extinguished (EXT) in a different context. On post-cocaine day 8, rats were re-exposed to the cocaine-paired context for 15 min to elicit memory reactivation (MR). They then received bilateral intra-BLA vehicle (VEH) or corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF; 0.2, 30, or 500 ng/0.5 μL per hemisphere) infusions. Cocaine-seeking behavior was assessed in the cocaine-paired context (Test) three days later, after at least two additional daily extinction training sessions in the extinction context. The schematics illustrate cannula placements in males (upper) and females (lower) in experiment 3. (B) Active and inactive-lever responses (mean ± SEM) in males (n = 6–11/group) in the cocaine-paired (COC) context during the MR session (before treatment) and upon first re-exposure to the extinction (EXT) and COC contexts at test (after treatment). (C) Time-course of active-lever responses (mean ± SEM) in males in the COC context at test. (D) Active- and inactive lever responses (mean ± SEM) in females (n = 8–14/group) in the COC context during the MR session (before treatment) and upon first re-exposure to the EXT and COC contexts at test (after treatment). (E) Time-course of active-lever responses (mean ± SEM) in females in the COC context at test. Symbols: Pound signs indicate difference from the extinction context, #ANOVA context main effect collapsed across treatment or time, or context simple-main effect in a treatment group, Tukey’s tests. Double daggers indicate difference from subsequent training sessions, ‡ANOVA time main effect independent of treatment. Silcrows indicate difference from males, §ANOVA sex main effect collapsed across treatment, §sex simple-main effect for a treatment condition, Tukey’s test. All ps < 0.05.