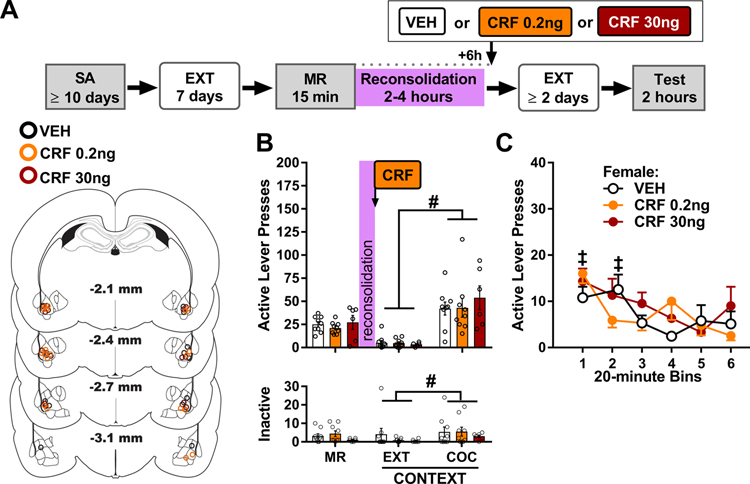
Figure 5. Intra-BLA CRF treatment in females 6 h after cocaine-memory reactivation does not alter drug context-induced cocaine seeking three days later.
(A) Experimental timeline. Female rats were trained to self-administer cocaine (SA) in a distinct context, and their lever responding was then extinguished (EXT) in a different context. On post-cocaine day 8, rats were re-exposed to the cocaine-paired context for 15 min to elicit memory reactivation (MR). Six hours after MR, they received bilateral intra-BLA vehicle (VEH) or corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF, 0.2 or 30 ng/0.5 μL per hemisphere) infusions. Cocaine-seeking behavior was assessed in the cocaine-paired context (Test) three days later, after at least two additional daily extinction training sessions in the extinction context. The schematic illustrates cannula placements in experiment 4. (B) Active- and inactive-lever responses (mean ± SEM) in females (n = 6–9/group) in the cocaine-paired (COC) context during the MR session (before treatment) and upon first re-exposure to the extinction (EXT) and COC contexts at test (after treatment). (C) Time-course of active-lever responses (mean ± SEM) in females in the COC context at test. Symbols: Pound signs indicate difference from the extinction context, #ANOVA context main effect collapsed across treatment. Double daggers indicate difference from subsequent training sessions, ‡ANOVA time simple-main effect in a treatment group. All ps < 0.05.