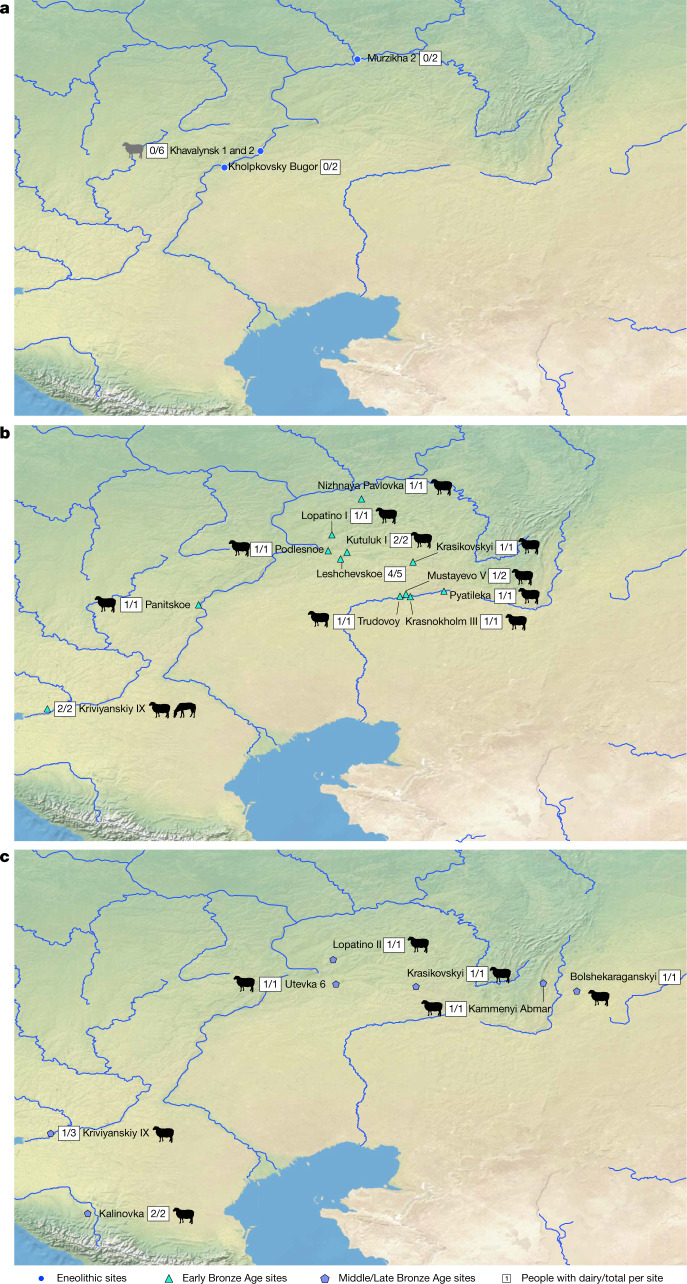
Fig. 1. Map showing sites that yielded individuals with preserved ancient proteins.
a–c, Eneolithic (a), Early Bronze Age (b) and Middle–Late Bronze Age (c) sites in the Pontic–Caspian region, showing the number of individuals with a positive dairy identification out of the total number of individuals with preserved ancient proteins for each site. Strong evidence of preservation of equine or ruminant milk protein identifiers are depicted with black animal icons; the single individual with equivocally identified casein peptides is shown with a grey icon. For a map of all sites (including those without preserved proteins), see Supplementary Fig. 1. Base maps were created using QGIS 3.12 (https://qgis.org/en/site/), and use Natural Earth vector map data from https://www.naturalearthdata.com/downloads/. The horse image is reproduced from ref. 33; sheep silhouette, public domain (https://thenounproject.com/icon/12538/).