Figure 1.
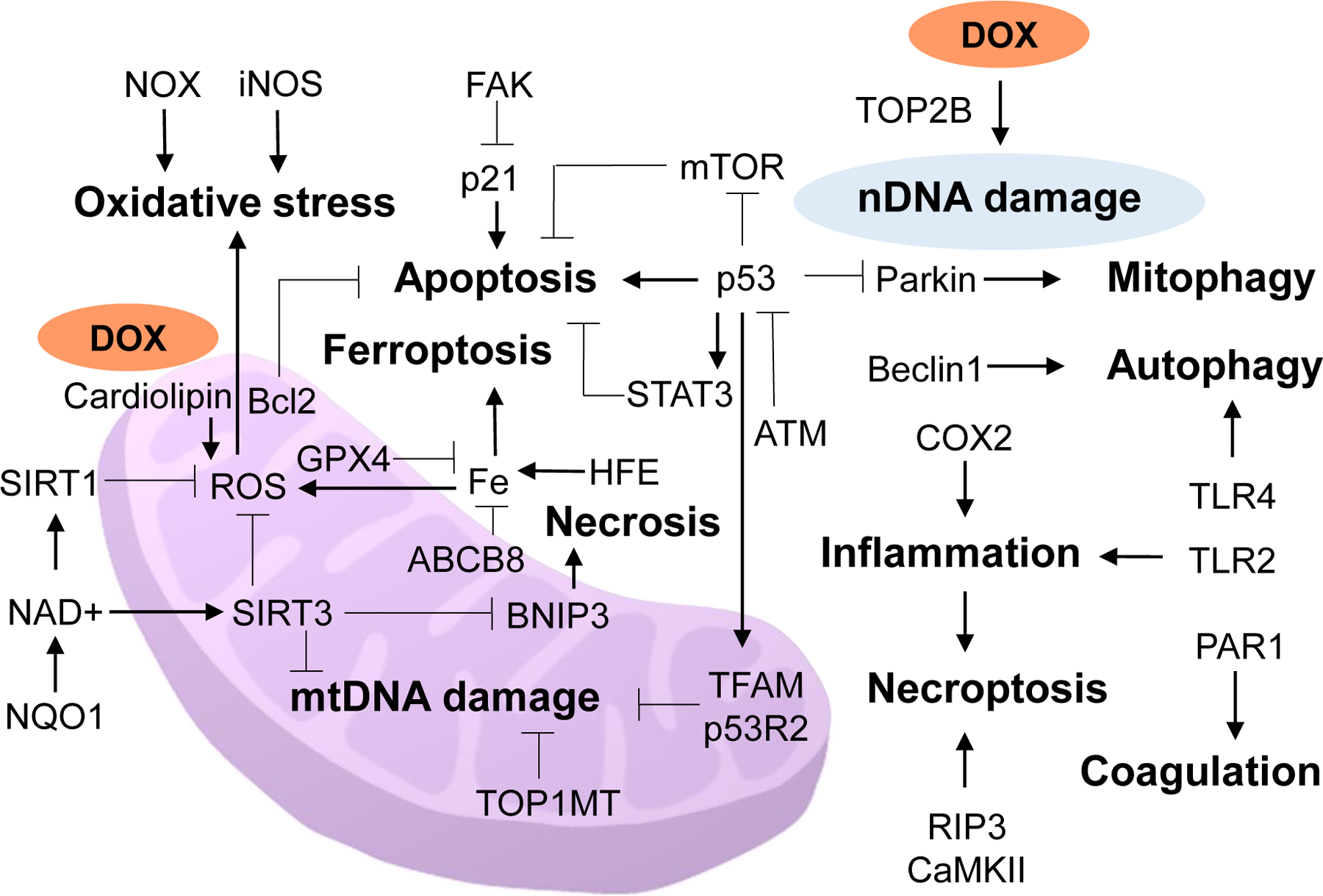
Schematic diagram of the major cellular processes (bold print) and their mediators/pathways of anthracycline cardiotoxicity. ABCB8, ATP binding cassette subfamily B member 8; ATM, ataxia telangiectasia mutated kinase; Bcl2, B-cell lymphoma 2; BNIP3, Bcl2 interacting protein 3; CaMKII, calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II; COX-2, cyclooxygenase 2; DOX, doxorubicin; FAK, focal adhesion kinase; GPX4, glutathione peroxidase 4; HFE, human homeostatic iron regulator protein; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; mtDNA, mitochondrial DNA; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; NOX, NAD(P)H oxidase; NQO1, NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase 1; nDNA, nuclear DNA; PAR1, protease-activated receptor 1; p53R2, p53-inducible ribonucleotide reductase; RIP3, receptor-interacting protein 3; SIRT, sirtuin; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; TFAM, transcription factor A, mitochondrial; TLR, toll-like receptor; TOP1MT, topoisomerase I mitochondrial; TOP2B, topoisomerase 2-beta.
