Figure 5. Two modified versions of the FR model recapitulate Drosophila search behavior around multiple fictive food sites.
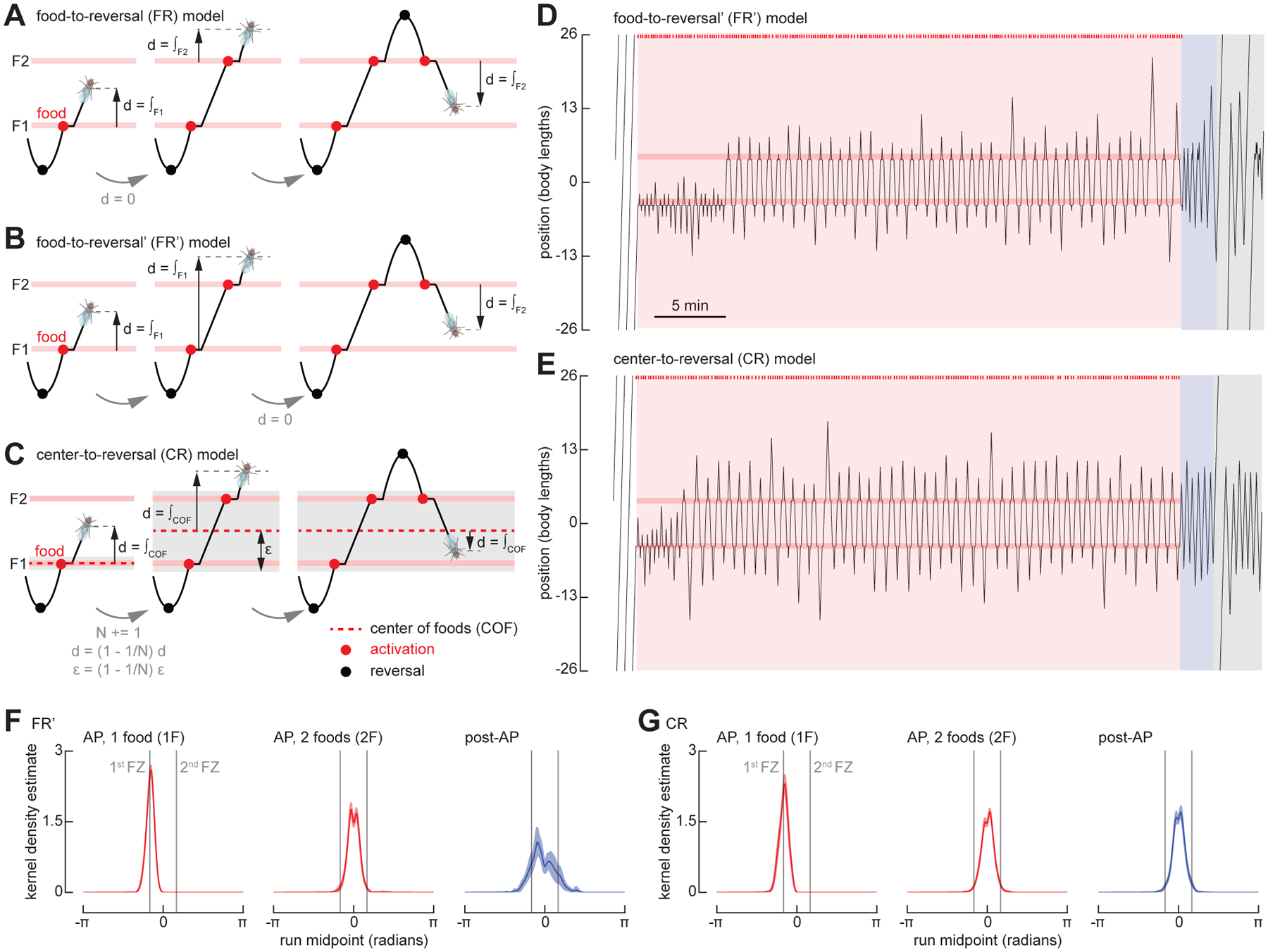
(A) Schematic, showing features of food-to-reversal (FR) model. The virtual fly resets its integrator at each new food that it encounters.
(B) As in (A) for food-to-reversal (FR’) model. The virtual fly resets its integrator at the first food encountered after each reversal.
(C) As in (A) for center-to-reversal (CR) model. The virtual fly resets its integrator at the center of all the food locations it encounters during a run.
(D) As in Figure 4A, for a simulation using the FR’ model.
(E) As in Figure 4A, for a simulation using the CR model. See also Video S4.
(F) As in Figure 4B, for simulations using the FR’ model. The first 300 simulations in which the virtual fly found both food sites are included. (N = 300).
(G) As in Figure 4B, for simulations using the CR model. The first 300 simulations in which the virtual fly found both food sites are included. (N = 300).
See also Video S4.
