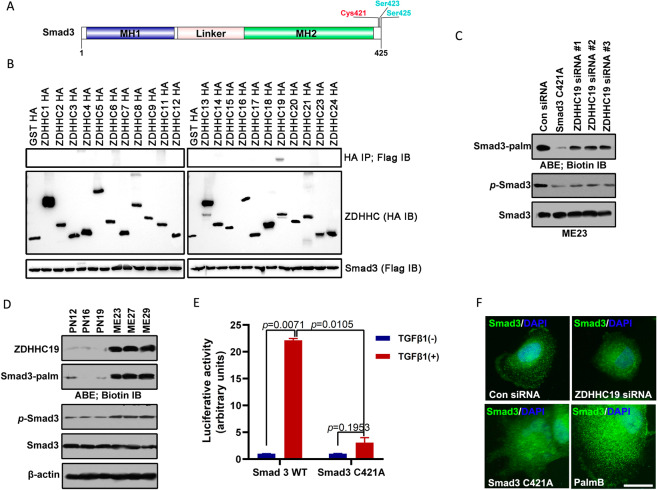
Fig. 3. Palmitoylation of Smad3 mediated by ZDHHC19 promotes its association with the plasma membrane and activation of the TGF-β pathway.
A Diagram showing the sites of palmitoylation of Smad3. CSS-Palm 4.0 software indicated that Cys421 was a potential palmitoylation site for Smad3. B HEK293 cells were co-transfected with constructs encoding Flag-Smad3 and HA-ZDHHCs in a 6-well plate. Cell lysates were harvested for immunoprecipitation by anti-Flag antibody and then for acyl–biotin exchange (ABE) and western blot analysis. The results of immunoblotting for total Smad3 and HA-ZDHHC proteins are shown. C Palmitoylation and phosphorylation of Smad3 in ME23 cells transfected with Smad3 C421A mutant constructs or infected with ZDHHC19 siRNA for 48 h. D Expression levels of ZDHHC19 and Smad3 and palmitoylation level of Smad3 in proneural and mesenchymal GSCs. E The Smad3 palmitoylation mutant suppressed activation of the TGF-β/Smad-signaling pathway. ME23 cells were stably transfected with (SBE)4-luc, which can be activated by TGF-β1. These ME23 cells were then transfected with Smad3 or Smad3 C421A and stimulated with 5 ng/ml TGF-β1 for 18 h starting 24 h after transfection. F Expression of Smad3 in ME23 GSCs (monolayer culture) transfected with ZDHHC19 siRNA or Smad3 C421A mutant plasmid or treated with the de-palmitoylation inhibitor, PalmB (1 μM) for 48 h was analyzed by immunofluorescence staining. Scale bar, 100 μm. GSCs glioblastoma stem cells.