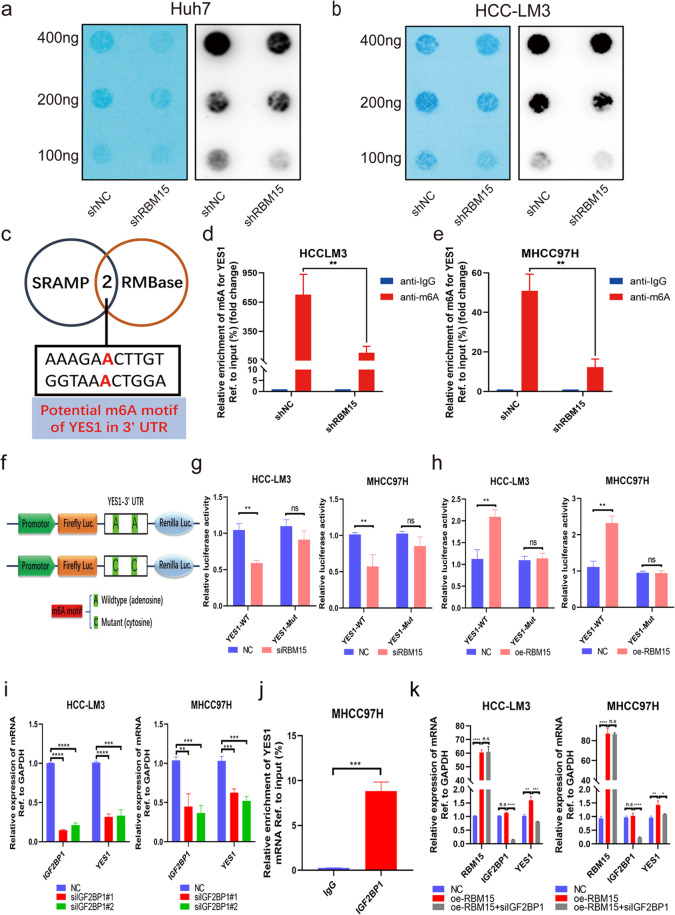
Fig. 5. RBM15 regulates YES1 in an IGF2BP1-m6A-dependent pattern.
a, b Global m6A level of RNA extracted from RBM15-knockdown Huh7 and HCC-LM3 cells was investigated by m6A dot blot assays. The intensity of dot immunoblotting indicated the m6A level of total RNAs, while methylene blue staining was applied to measured input RNA; c a Venn diagram was generated for predicting potential m6A motif of YES1 in 3’ UTR from SRAMP and RMBase databases. Two candidate m6A motifs were selected; d, e showed m6A modification of YES1 by MeRIP-qPCR analyses in HCC-LM3 and MHCC97H cells. Knockdown of RBM15 induced a decreased m6A abundance on YES1 compared with the control group (**p < 0.01; t test); f construction pattern of luciferase reporters. The wild-type or mutant type (m6A motif mutated) sequence of YES1 3’ UTR was inserted into a pcDNA 3.1 vector, which contained Firefly and Renilla elements; g relative luciferase activity of the wild-type or mutant group was determined in RBM15-silenced HCC-LM3 and MHCC97H cells (normalized to Renilla activity; **p < 0.01; t test); h relative luciferase activity of the wild-type or mutant group was determined in RBM15 overexpression HCC-LM3 and MHCC97H cells (normalized to Renilla activity; **p < 0.01; t test); i YES1 mRNA expression was decreased after knockdown of IGF2BP1 in HCC-LM3 and MHCC97H cells (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001; t test). j RIP-qPCR validated that YES1 mRNA could bind to IGF2BP1 protein (***p < 0.001; t test); k the upregulation YES1 mRNA induced by RBM15 overexpression was reduced by knockdown of IGF2BP1 (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001; t test). The data are presented as mean ± SD.