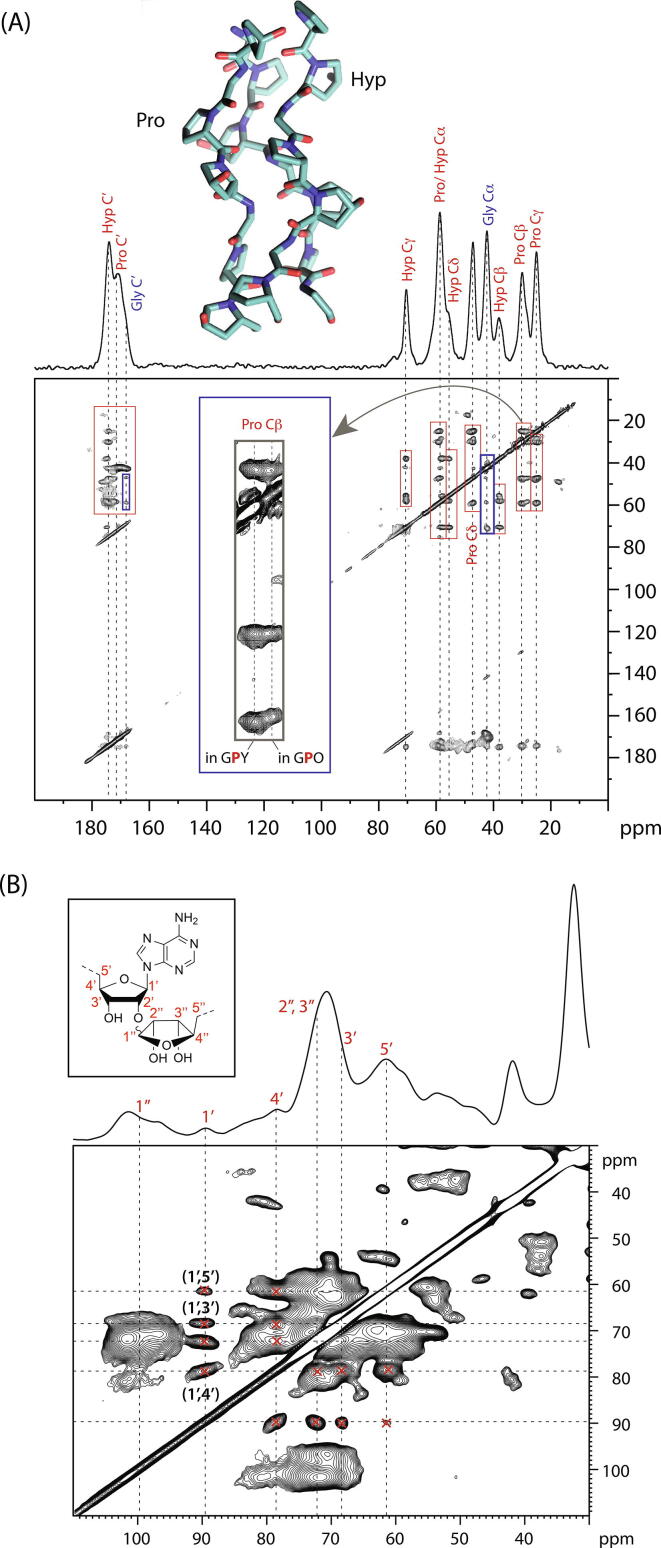
Fig. 2.
(A) A 2D 13C-13C correlation NMR spectrum (proton-driven spin-diffusion) of in vitro ECM from foetal sheep osteoblasts in which U-13C-Pro, Gly were used in the cell culture media, resulting in ECM proteins in which Gly, Pro and Hyp are extensively 13C-labelled. Correlation signals from these (primarily collagen) residues thus appear in this 2D correlation spectrum. Intraresidue signals are indicated in red rectangles and inter-residue correlations in blue rectangles. The inset (grey rectangle) is an expansion of the Pro C signals, showing they can be resolved into those from Pro in GPO and more general GPY triplets. The 1D 13C MAS NMR spectrum of the same sample is shown at the top. (B) 2D 13C-13C correlation NMR spectrum (proton-driven spin-diffusion) of in vitro calcifying (bovine) vascular smooth muscle cell ECM showing assignments of some of the correlation signals from poly(ADP ribose) (inset: structure of one monomer unit of poly(ADP ribose) showing the 13C site labelling scheme). The 1D 13C projection of the spectrum is shown above the 2D spectrum. The poly(ADP ribose) signals are not resolved from other glycan species in this 1D spectrum, although they are well-resolved in the 2D spectrum, showing the power of 2D NMR correlation spectroscopy.