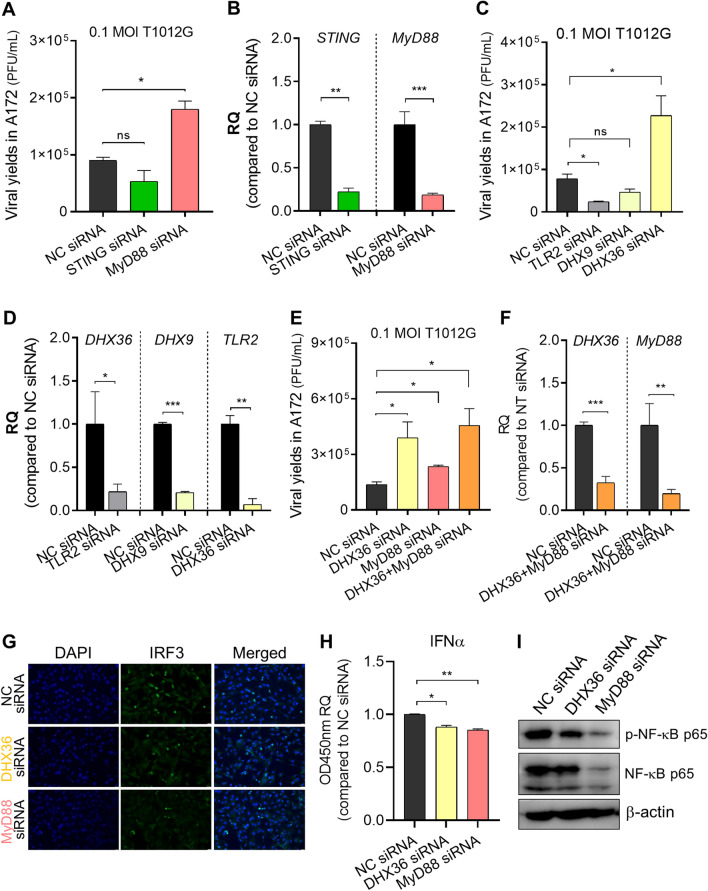
Figure 5.
Identification of immune factors responsible for increased virus production in the resistant cell line A172 mediated by Mx2 depletion. (A–F) A172 cells were transfected with indicated siRNAs or NC siRNA, followed by exposure to 0.1 MOI oHSV-1 T1012G for 2 h at 24 h post-transfection. Virus progeny were harvested at 24 h post-infection and titered in Vero cells. (A) Viral yields in MyD88 or STING-depleted A172 cells; (C) Viral yields in DHX36, DHX9 or TLR2-depleted A172 cells; (E) Viral yields in MyD88, DHX36 or both-depleted A172 cells; (B,D,F) Knockdown efficiency of MyD88, STING, DHX36, DHX9 and TLR2 siRNA were analyzed by the qPCR assay. RQ: relative quantity, compared to transcript levels in NC siRNA-transfected A172 cells. Error bars represent SD. GAPDH serves as a normalization control. A172 cells were depleted of DHX36, MyD88 or mock-depleted by siRNA transfection, 24 h later, cells were harvested for the following indicated tests. (G) Investigation of nuclear IRF3 in A172 cells via immunofluorescence staining. (H) ELISA quantification of secreted IFNα in cell supernatant. RQ: relative quantity, values that correspond to optical densities at OD 450 nm compared to values in NC siRNA-transfected A172 cells. (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; compared with NC siRNA-treated A172 cells. Error bars represent SD.) (I) Expression of effector proteins associated with the NF-κB signaling pathway. Blots were cut and probed with indicated antibodies, respectively. β-actin serves as a loading control.