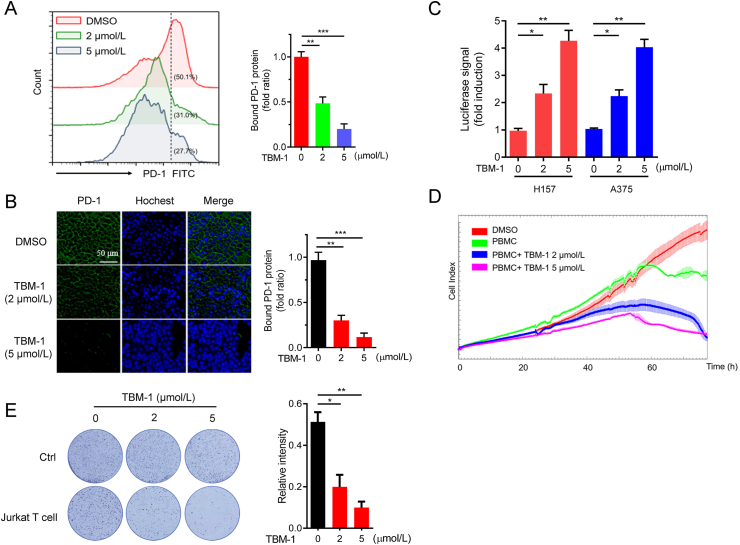
Figure 2.
TBM-1 attenuates the ability of tumor cell binding PD-1 and enhances the cytotoxicity of T cells. (A) PD-1 binding to H157 cells treatment with indicated doses of TBM-1 for 24 h was measured by flow cytometry. The y axis represents the MFI of PD-1. (B) Immunostaining of recombinant Fc-PD-1 on H157 cells treated with TBM-1 (2 and 5 μmol/L, 24 h). The nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33,342. (Scale bar, 50 μm). The intensity of green fluorescence indicates bound PD-1. (C) The PD-1/PD-L1 interaction between Jurkat NFAT-luciferase reporter cells and H157 or A375 cells treated with TBM-1 (2 or 5 μmol/L) for 16 h was detected by PD-1/PD-L1blockade assay. Data are presented as fold induction over untreated control. (D) Human PBMC cells toward cancer cells killing in H157 cells treated with TBM-1 (2 or 5 μmol/L) for 24 h were analyzed by cell impedance assay. (E) Activated Jurkat T cell and H157 cells were co-cultured in 12-well plates for 2 days in the presence of TBM-1. Crystal violet staining was used to monitor the surviving cancer cells. Relative surviving cell intensity is shown at the right. Data are presented as mean ± SD, n = 3; ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001.