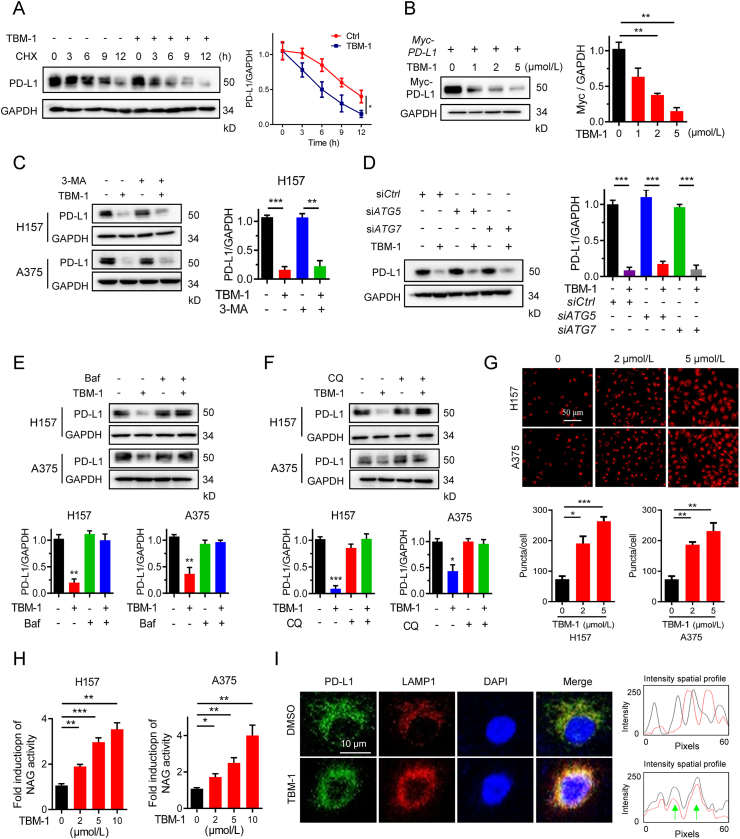
Figure 4.
TBM-1 induces lysosome-dependent degradation of PD-L1. (A) Immunoblotting detecting the PD-L1 abundance in H157 cells treatment with DMSO or TBM-1 (5 μmol/L) for the indicated time periods in the presence of CHX (25 μg/mL). The PD-L1 abundance was normalized to GAPDH and quantification of PD-L1 intensity is shown on the right. (B) Myc-PD-L1 was transfected to H157 cells for 24 h, followed by TBM-1 treatment for 16 h. The level of Myc-PD-L1 was measured by immunoblotting. Quantification of Myc-PD-L1 to GAPDH was shown at the right. (C) Immunoblotting detecting the PD-L1 level in H157 and A375 cells pre-treated with indicated dose of 3-MA (10 mmol/L), followed by 5 μmol/L TBM-1 treatment for 24 h. Quantification of PD-L1 to GAPDH was shown at the right. (D) H157 cells were transfected with indicated siRNAs for 48 h, followed by TBM-1 (5 μmol/L) treatment for 24 h. The PD-L1 level was measured by immunoblotting. Quantification of PD-L1 to GAPDH was shown at the right. (E) and (F) Immunoblotting determining the PD-L1 level in H157 and A375 cells pre-treated with indicated dose of Baf (25 nmol/L) (E), or CQ (20 μmol/L) (F) followed by 5 μmol/L TBM-1 treatment for 24 h. Quantifications of PD-L1 to GAPDH were shown on the bottom. (G) Images and quantification of LysoTracker Red in H157 and A375 cells treatment with TBM-1 (2 or 5 μmol/L) for 12 h (scale bar, 50 μm). Quantification of LysoTracker Red staining is shown. (H) H157 and A375 cells were treated with indicated doses of TBM-1 for 6 h and lysosomal NAG activities were measured. (I) Immunofluorescence analyzing the co-localization between PD-L1 and LAMP-1 in H157 cells treatment with TBM-1 (5 μmol/L) for 12 h. The intensity profiles of PD-L1 and LAMP1 are shown in the right panel, with the co-localizing sites marked by green arrows. Data are presented as mean ± SD, n = 3; ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001.