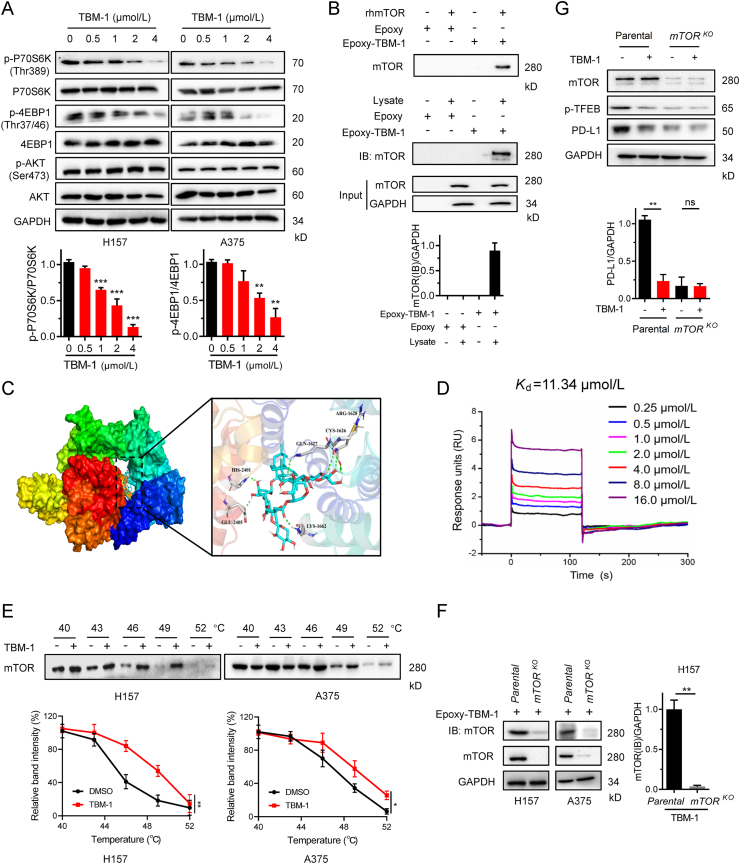
Figure 6.
TBM-1 binds to mTOR and inactivates its activity. (A) Immunoblotting determining the phosphorylation of p70S6K, 4EBP1 and AKT in H157 and A375 cells treatment with indicated doses of TBM-1 for 12 h. Quantifications of p-P70S6 K and p-4EBP1 are shown on the bottom. (B) Recombinant human mTOR (rhmTOR) or H157 cell lysate was incubated with Epoxy-activated sepharose beads (Epoxy) or TBM-1-immobilized Epoxy-activated Sepharose beads (Epoxy-TBM-1) and then immunoblotted with anti-mTOR antibody. Quantification of mTOR to GAPDH was shown on the bottom. (C) Molecular docking model revealed that TBM-1 binds to the FRB domain of mTOR. (D) SPR analysis of the TBM-1 and mTOR binding. The activated CM5 sensor chip was used to immobilize the recombinant human mTOR protein and flowed across TBM-1. (E) CETSA indicating mTOR target engagement by TBM-1 in H157 cells and A375 cells. Quantification of the thermal stability of mTOR was indicated on the bottom. (F) Parental and mTORKO H157 cell lysates were incubated with TBM-1-immobilized epoxy-activated sepharose beads and then immunoblotted with anti-mTOR antibody. (G) Parental and mTORKO H157 cells were treated with 5 μmol/L TBM-1 for 12 h. The levels of TFEB ser211 phosphorylation and PD-L1 were measured by immunoblotting. Quantification of PD-L1 to GAPDH was shown on the bottom. Data are presented as mean ± SD, n = 3; ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01.