Figure 6.
Modulating positive and negative regulators of Wg signaling pathway affects the L mutant phenotype
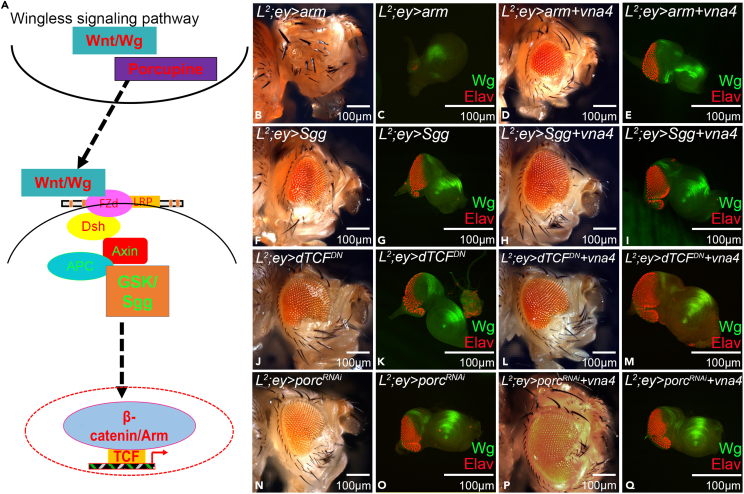
(A) Schematic presentation of the Wg signaling pathway showing various members of the canonical pathway. The positive regulators are in red, and negative regulators of the Wg pathway are in green.
(B–E) Activating Wg signaling in the L2 mutant eye background by misexpression of (B and C) arm alone (L2/+; ey>arm), (D and E) arm and vna4 (L2/+; ey>arm; vna4). Note that vna4 misexpression with arm (L2/+; ey>arm; vna4) in the eye rescues the L2/+; ey>arm reduced eye phenotype.
(F–M) Blocking Wg signaling in L2 mutant eye background by misexpression of (F and G) sgg alone (L2/+; ey>sgg), (J and K) dTCFDN alone (L2/+; ey> dTCFDN) results in rescue of L2 loss-of-ventral eye phenotype. Similarly, in L2 mutant background misexpression of vna4 along with (H and I) sgg (L2/+; ey>sgg; vna4) and (L and M) dTCFDN (L2/+; ey> dTCFDN; vna4) significantly rescue the partial loss-of-ventral eye phenotype.
(N–Q) Blocking transport of Wg morphogen in L2 mutant eye background by misexpression of (N and O) porcRNAi alone (L2/+; ey> porcRNAi), (P and Q) porcRNAi and vna4 (L2/+; ey> porcRNAi; vna4). Note that L2/+; ey> porcRNAi exhibits weak rescue of loss-of-ventral eye phenotype whereas vna4 misexpression with porcRNAi (L2/+; ey> porcRNAi; vna4) enhances the phenotype strength. All the images are displayed in same polarity as dorsal domain-towards the top, and ventral domain-towards the bottom. Scale bar = 100 μm. See also Figures S13 and S14.