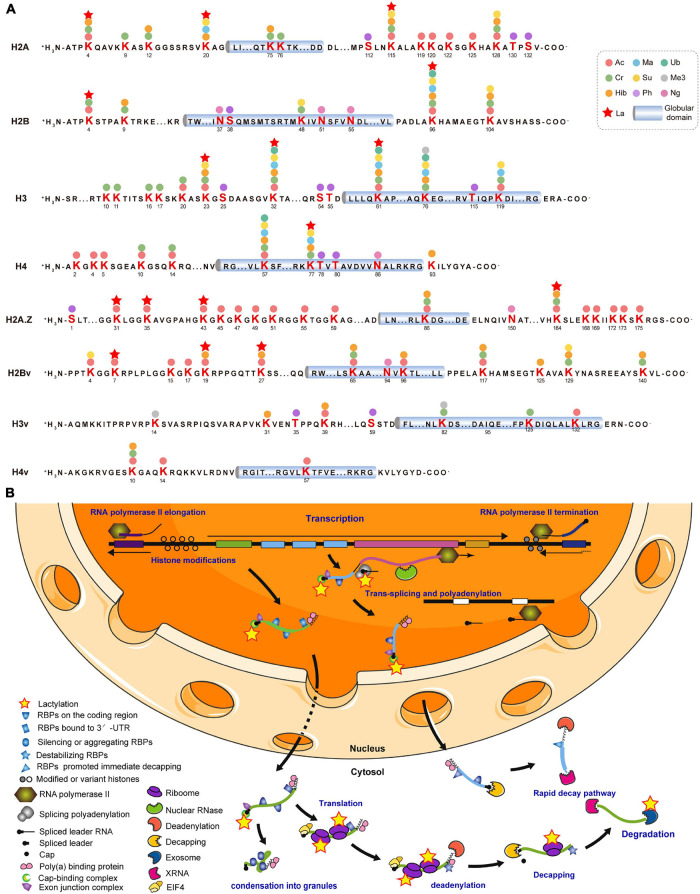
FIGURE 3.
Lysine lactylation occurs on histones and gene regulators. (A) Cylinders indicate globular histone domains. Mature histone sequence is shown with modified residues in bold. Numbers represent amino acid positions after initial Met was removed. (B) This diagram is modified from Clayton (2016, 2019). Multiple ORFs lacking introns are arranged in a head-to-tail manner with some tandem repeats and occasional directional changes (Clayton, 2016). Most RNA Pol II transcription is initiated in DNA stretches several kilobases in length, separating gene arrays orientated in opposite, diverging directions. Initiation and termination regions are enriched with modified and variant histones. Pre-mRNA is processed into mature mRNAs by trans-splicing capped spliced leader and polyadenylation. Completed mRNA is exported to cytosol with bound poly (A) binding protein (PABP; Zoltner et al., 2018), exon junction complex (EJC; Bercovich et al., 2009), and nuclear cap-binding complex (CBC; Freire et al., 2017). Certain untranslated mRNAs bind and silence or induce the aggregation of RBPs, followed by condensation into granules. Mature mRNA binding by EIF4 is followed by translation (Dhalia et al., 2006). Stabilizing RBP is replaced by destabilizing RBP, followed by deadenylation (Schwede et al., 2009). After decapping, mRNA is degraded by XRNA and exosome (Fadda et al., 2013). A subset of mRNAs is immediately degraded. Kla proteins are represented by yellow pentagrams. RBPs are unlabeled but listed in Supplementary Table 5.