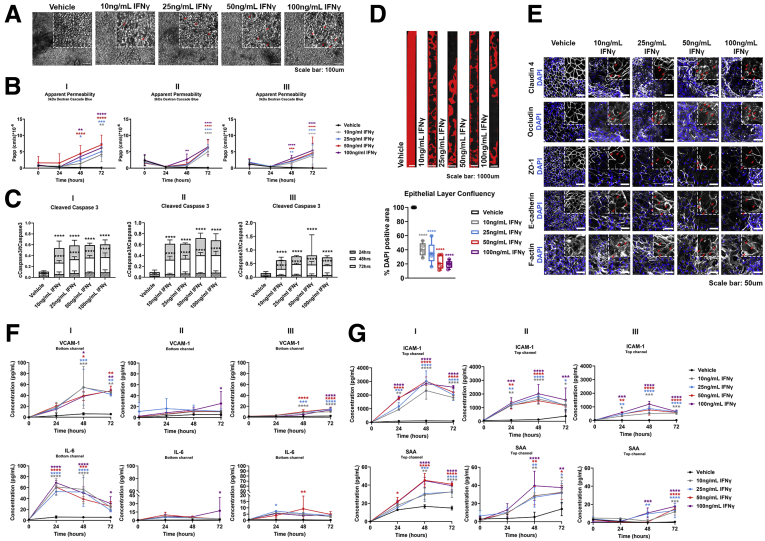
Figure 7.
The established epithelial barrier responds in a time- and concentration-dependent manner to IFNγ, a barrier-disruptive agent. (A) Representative phase-contrast images of the colonic epithelial monolayer 48 hours after treatment with IFNγ. Gradual degeneration of the morphology of the epithelial cells was observed as the concentration of IFNγ increased, indicating a transition from columnar to the squamous-shaped epithelium (red arrows). (B) The Papp of epithelial cells to 3 kilodaltons dextran Cascade blue, over the course of 72 hours of basolateral stimulation with IFNγ, indicates a dose-, donor-, and time-dependent barrier disruption. Data shown correspond to 1 representative of 3 independent experiments. n = 3–12 chips/condition, means ± 95% CI, 2-way analysis of variance, Tukey post hoc test. (C) Quantification of the cleaved over total caspase 3 in epithelial cells shows a significant and concentration-dependent activation of apoptosis 48 and 72 hours after stimulation across 3 different donors. n = 3 chips/condition means ± 95% CI, 2-way analysis of variance, Tukey post hoc test. (D) Representative tile fluorescent images highlighting the area of the Colon Intestine-Chip covered with epithelial cells, determined by positive 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) staining (red), 48 hours after stimulation with different concentrations of IFNγ. The epithelial layer confluency is expressed as a percentage of the DAPI-positive area over the total area of the chip, depicted as a box plot where each individual point represents a single chip. A significant and concentration-dependent decrease of the epithelial layer confluency was observed 48 hours after treatment with IFNγ. n = 4–5 chips/condition, means ± 95% CI, 1-way analysis of variance, Tukey post hoc test. (E) Representative confocal immunofluorescence images indicating the dose-dependent degeneration of the epithelial TJs, as shown by the redistribution of claudin 4, ZO-1, and F-actin, and internalization of occludin and E-cadherin (red arrows). Cell nuclei are shown in blue. (F) Time-course quantification of cytokines and vascular injury-related serum proteins in the Colon Intestine-Chip shows a concentration-, donor-, and time-dependent secretion of IL6 and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) in the bottom channel, upon treatment with IFNγ. n = 3 chips/condition, means ± SD, 2-way analysis of variance, Tukey post hoc test. (F) Time-course quantification of vascular injury-related serum proteins in the Colon Intestine-Chip shows a concentration-, donor-, and time-dependent secretion of intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and serum amyloid A (SAA) in the top channel, upon treatment with IFNγ. n = 3 chips/condition, means ± SD, 2-way analysis of variance, Tukey post hoc test. ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001, and ∗∗∗∗P < .0001.