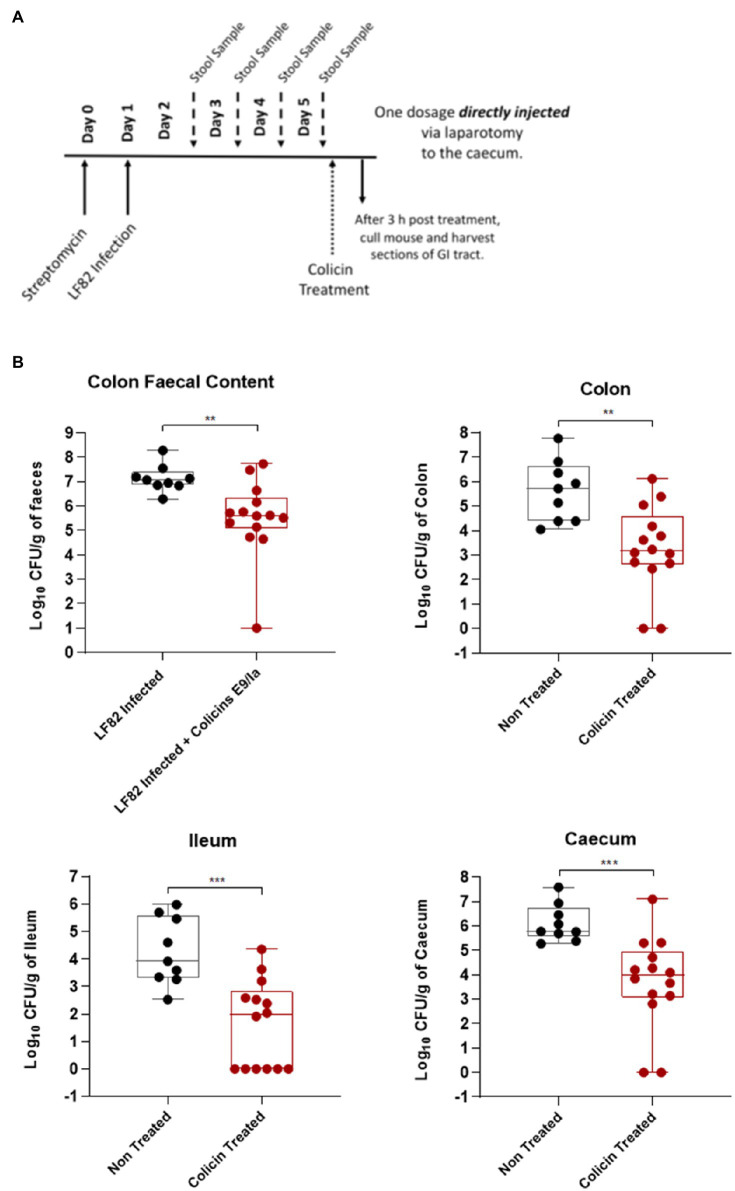
Figure 2.
Direct administration of a colicin cocktail reduces levels of LF82 colonization of infected mice. An Escherichia coli LF82StrpR murine infection model was used to assess the efficacy of a colicin cocktail treatment directly administered to the caecum via laparotomy. Four days after LF82StrpR challenge, mice were treated with the administration via laparotomy of 50μl of a combination of E9 and Ia (0.5mg ml−1 each) or 50μl of PBS (control group). (A) Experimental scheme. (B) Levels of LF82StrpR strain in both control (black, n=10) and colicin treated (red, n=14) groups for the different sections of the GI tract. Statistical analysis was carried out for each subset using a Mann–Whitney test between LF82StrpR infected and colicin-treated groups. **p<0.002, ***p<0.0004.