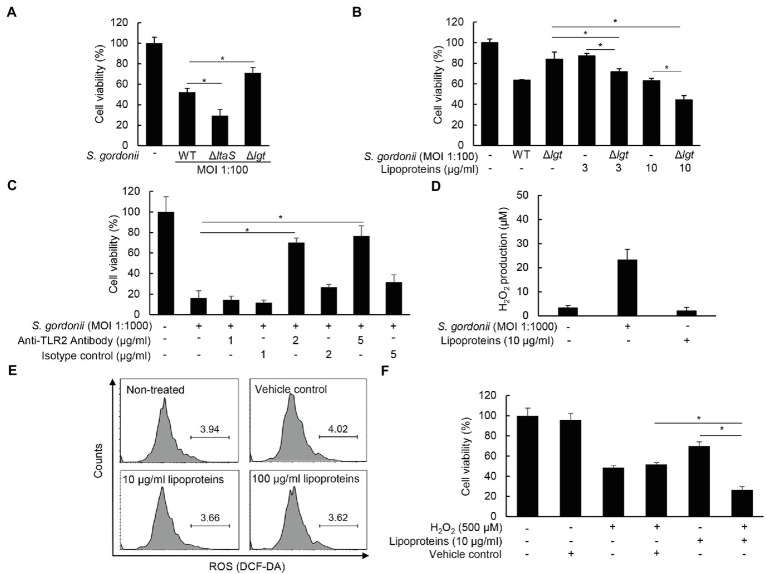
Figure 6.
S. gordonii lipoproteins contribute to the cytotoxicity of PDL cells in cooperation with H2O2. (A) PDL cells were treated with S. gordonii wild-type, its ΔltaS, and Δlgt at MOI 1:100 for 3 h. (B) PDL cells were treated with S. gordonii wild-type or its Δlgt at MOI 1:100 in the presence or absence of S. gordonii lipoproteins (3 or 10 μg/ml) for 3 h. (C) PDL cells were pre-treated with anti-TLR2 antibody (0, 1, 2, or 5 μg/ml) for 1 h, followed by treatment with S. gordonii at MOI 1:1000 for 3 h. Trypan blue assay was used to determine the number of viable cells. (D) PDL cells were treated with S. gordonii at MOI 1:1000 or S. gordonii lipoproteins (10 μg/ml) for 1 h. The level of H2O2 in the supernatant was determined using a hydrogen peroxide assay kit. (E) PDL cells were treated with 10 µM of DCF-DA for 30 min at 37°C. The DCF-DA-treated cells were washed with PBS and then treated with S. gordonii lipoproteins (10 or 100 μg/ml) for 3 h in a CO2 incubator. Fluorescent intensity was analyzed by flow cytometry. (F) PDL cells were treated with S. gordonii lipoproteins (10μg/ml) in the presence or absence of H2O2 for 3h. Trypan blue assay was used to determine the number of viable cells. One of three similar results is shown. *p < 0.05.