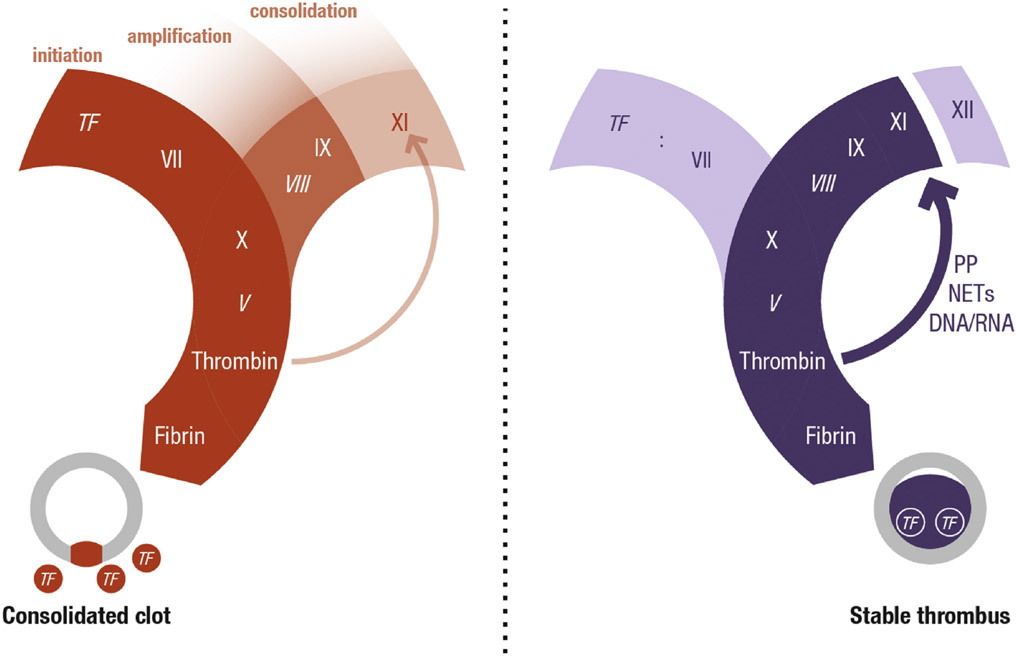
CENTRAL ILLUSTRATION. Hemostasis and Thrombosis.
Schematic representation of the key differences between hemostasis and thrombosis showing coagulation factor activation pathways and cross sections of a blood vessel. Two related but distinct processes of coagulation are represented, one characterized by clot formation to seal off a vessel wall injury (hemostasis) and the other by intraluminal clot formation resulting in obstruction of blood flow (thrombosis). Tissue factor initiates both processes but, whereas FXI plays a subsidiary role in hemostasis, in thrombosis FXI is required for thrombus growth within the vessel lumen. The predicted relative importance of the pathway components is denoted by the intensity of shading. Italics denote cofactors. NETs = neutrophil extracellular traps; PP = polyphosphate; TF = tissue factor.