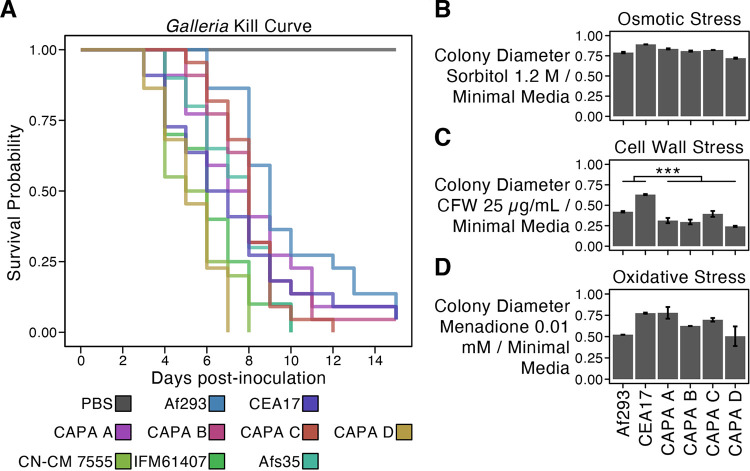
FIG 5.
Strain heterogeneity among COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis (CAPA) isolates of Aspergillus fumigatus. (A) The virulence of the CAPA isolates, reference strains Af293 and CEA17, and clinical strains Afs35, CN-CM7555, and IFM61407 significantly varied in the Galleria moth model of disease (P < 0.001; log-rank test; ≥20 replicates per strain). Pairwise examinations revealed CAPA isolate D was significantly more virulent than all other strains (Benjamini-Hochberg adjusted P < 0.01 when comparing CAPA isolate D to another isolate; log-rank test) with the exception of clinical strains IFM61407 and CN-CM 7555 (P = 0.085 and P = 0.386, respectively). Growth of CAPA isolates and references strains Af293 and CEA17 in the presence of osmotic (B), cell wall (C), and oxidative stressors (D). Growth differences between CAPA isolates and reference strains Af293 and CEA17 were observed across all growth conditions (P < 0.001; multifactor ANOVA). Pairwise differences were assessed using the post hoc Tukey’s honestly significant difference (HSD) test and were only observed for growth in the presence of CFW at 25 μg/ml (P < 0.001; Tukey HSD test) in which the CAPA isolates did not grow as well as the reference isolates. To correct for strain heterogeneity in growth rates, radial growth in centimeters in the presence of stressors was divided by radial growth in centimeters in the absence of the stressor (MM only). Abbreviations of cell wall stressors are as follows: CFW, calcofluor white; CR, Congo red; CSP, caspofungin. Growth in the presence of other stressors is summarized in Fig. S4. Error bars in panels B to D represent the average of ± one standard deviation across three replicates.