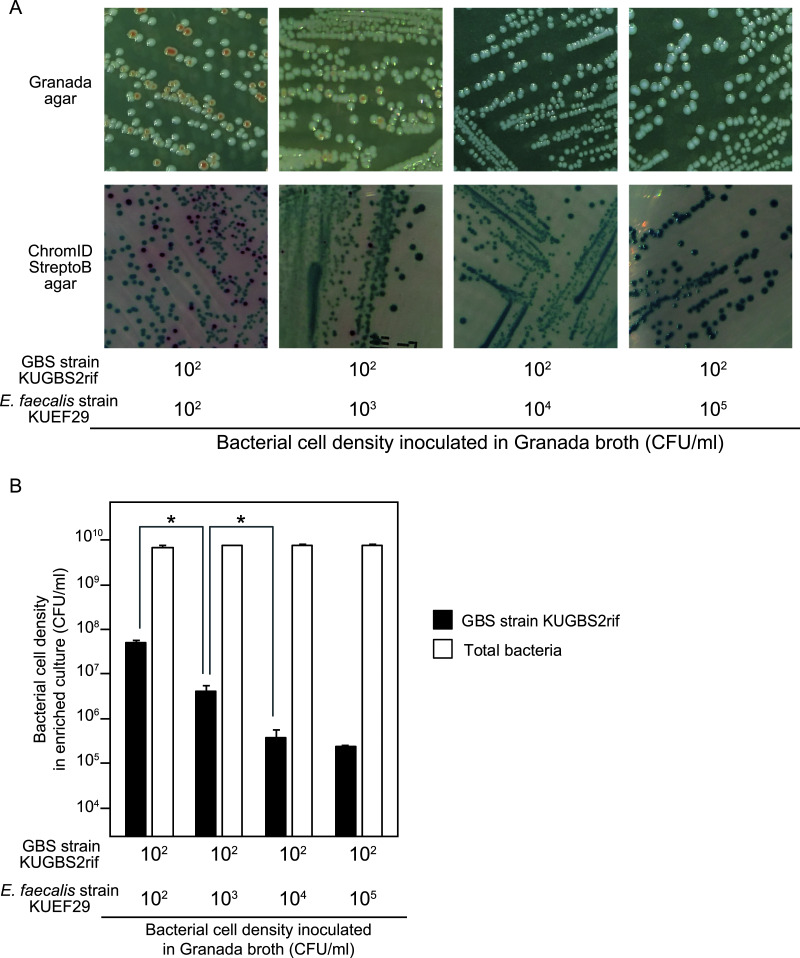
FIG 2.
Construction of the false-negative model by coculturing GBS KUGBS2rif with Enterococcus faecalis KUEF29. GBS KUGBS2rif at 102 CFU/ml was cocultured with E. faecalis KUEF29 at 102, 103, 104, and 105 CFU/ml in the Granada broth at 37°C for 24 h. The enriched culture was subcultured onto the Granada agar and the commercial chromogenic agar by stroke smear. (A) Colony appearance on Granada agar and commercial chromogenic agar. The GBS colony appeared orange on the Granada agar (top) and red on commercial chromogenic agar (bottom). GBS was detectable when KUGBS2rif at 102 CFU/ml was inoculated with KUEF29 at 102 and 103 CFU/ml in Granada broth, whereas it was not detected with KUEF29 at ≥104 CFU/ml. (B) Bacterial cell densities in the enriched cultures. The mean and SD of cell densities of KUGBS2rif (closed column) and total bacteria (open column) are presented with error bars (n = 3). Cell densities of total bacteria were measured to validate the experiment. According to one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), no statistical difference was observed in the total bacteria (P > 0.05), while it was observed in the KUGBS2rif (P < 0.0001). According to the following Tukey’s post hoc test, the GBS densities decreased with statistical significance, as the inoculated densities of E. faecalis increased from 102 and 103 to 104 CFU/ml. Statistical significance is denoted by an asterisk (*, P < 0.001).