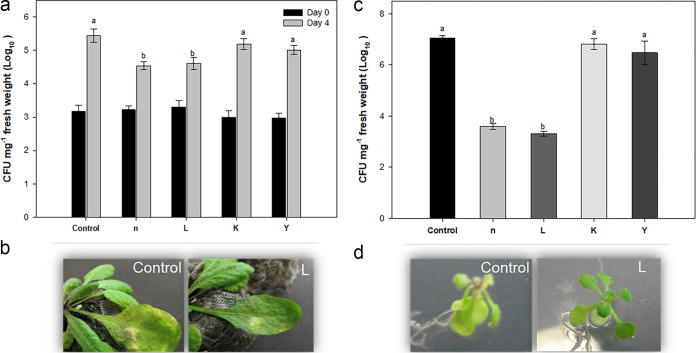
FIG 1.
Effects of treatment of Arabidopsis wild-type Col-0 with isolated rhizobacteria on resistance against a bacterial pathogen. In the in planta experiment, 4-week-old plants were challenge infected with P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000. (a and b) The growth of P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 (a) and disease symptoms (b) in control and rhizobacterium-treated plants were investigated. (c and d) An in vitro experiment showed significant reduction in disease symptoms in seedlings treated with rhizobacteria (d), as confirmed by the inhibition of P. syringae pv. tomato growth (c). The number of bacteria in the leaves was determined at 7 days after drop inoculation with a suspension at 109 CFU ml−1 in a plate assay. Different letters indicate statistically significant differences among treatments (P < 0.01). Bars indicate means ± standard errors from three independent experiments, with 12 inoculated leaves per treatment.