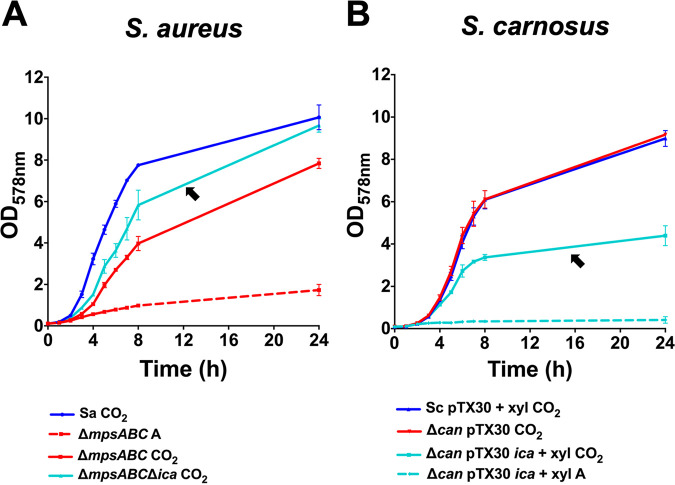
FIG 4.
The influence of biofilm mediated by polysaccharide intercellular adhesin (PIA) encoded by the ica operon in the growth of staphylococcal strains. (A) The growth of the S. aureus HG001 wild type (Sa), HG001 mpsABC deletion mutant (ΔmpsABC), and HG001 mpsABC and ica deletion mutant (ΔmpsABC ica) under atmospheric (A, dashed lines) and 5% CO2 (CO2, solid lines) conditions for 24 h. The arrow shows the ΔmpsABC Δica double mutant in which the biofilm-associated genes were deleted and which grew to a higher OD than the ΔmpsABC mutant alone in CO2. (B) The growth of the S. carnosus TM300 wild type (Sc) and TM300 carbonic anhydrase gene deletion mutant (Δcan) carrying empty plasmid pTX30 (as a control) under atmospheric (A, dashed lines) and 5% CO2 (CO2, solid lines) conditions for 24 h. The arrow shows the Δcan(pTX30) strain carrying the ica genes required for biofilm formation, which grew to a much lower OD than the Δcan strain alone in CO2 when induced by 0.7% xylose (xyl). All growth studies were performed using TSB. Each point in the graph is the mean ± SD from three independent biological replicates.