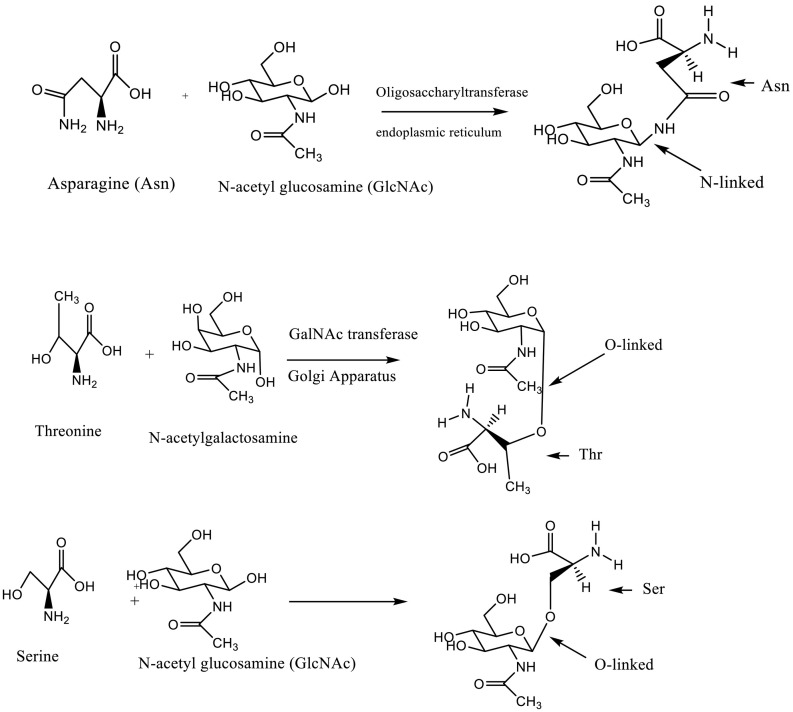
Fig. 4.
The amine functional group of asparagine (Asn) functions as a nucleophile to promote N-linked glycosylation, in which a carbohydrate chain (e.g., N-acetyl glucosamine (GlcNAc)) is added to the protein chain. In general, a carbohydrate chain is added to an Asn residue when it is flanked C-terminally by X-serine or X-threonine, where X is any amino acid other than proline. In the case of O-linked glycosylation, the hydroxyl group of threonine or serine acts as the nucleophile to promote conjugation of GlcNAc or N-acetyl galacosamine (GalNAc). See ref. [277].