Fig. 4 |. Experiment 2.
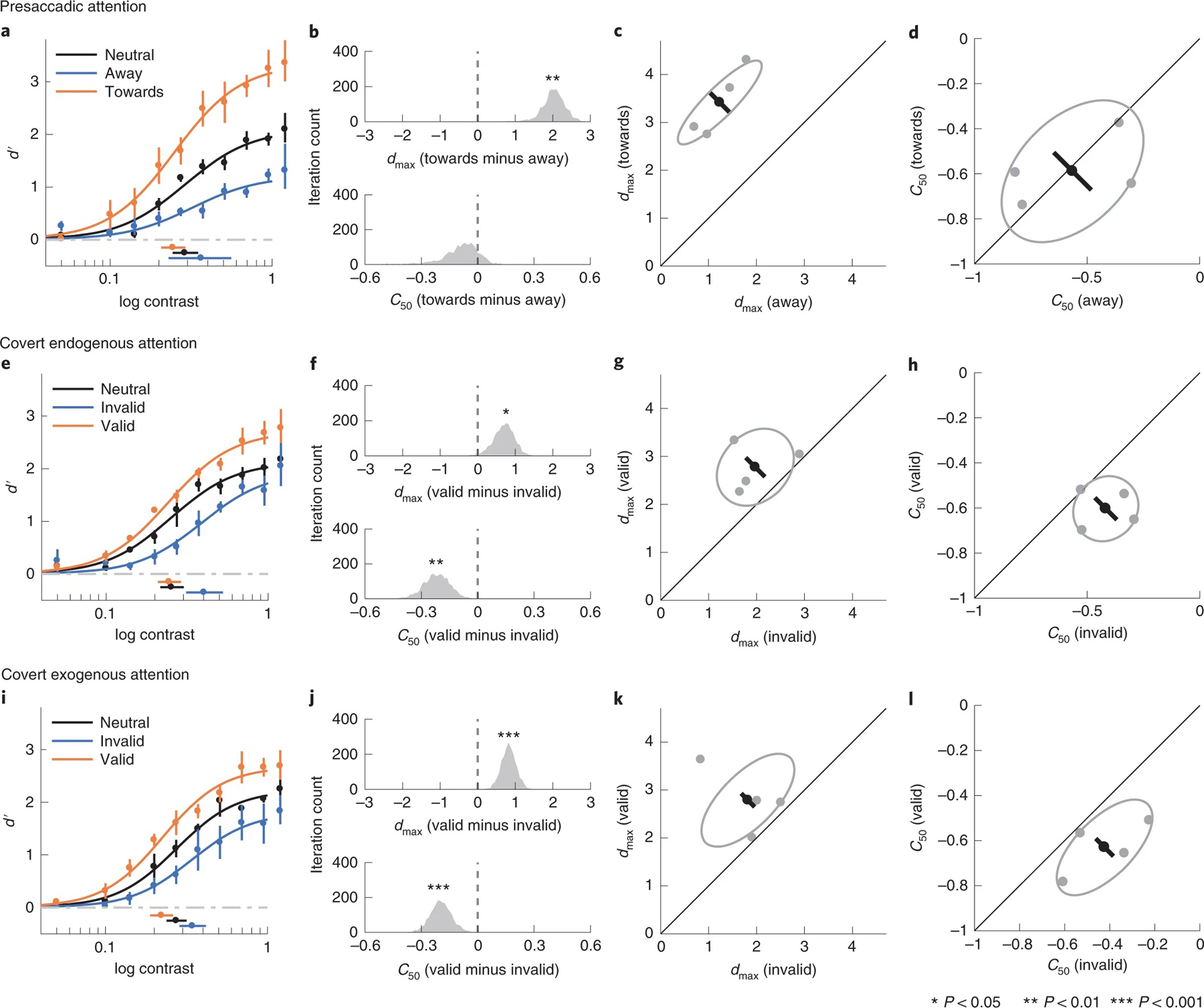
a–d, Presaccadic condition. a, Group-averaged psychometric functions (d′ versus contrast). dmax and C50 of the group-averaged psychometric functions are plotted to the right and bottom of the figure. The error bars represent the 95% bootstrapped confidence interval. b, The bootstrapped distribution of the difference of dmax (top) and the difference of C50 (bottom) between the towards and away conditions. Asterisks denote that the distribution is significantly different from zero. c, Grey dots, best-fitted dmax of individual observers; grey ellipse, the ellipse with the major axes oriented towards the difference and the sum of the dmax across two conditions. The difference (or sum) of dmax is first computed for individual observers; the major axis of the ellipse represents ±1 s.d. of the difference (or sum). The black dot shows the group-averaged dmax and the error bar represents the standard deviation of the bootstrapped distribution of the difference between the towards and away conditions. d, C50 illustrated in the same format as in c. e–h, Covert endogenous attention condition; corresponding to a–d. i–l, Covert exogenous attention condition; corresponding to a–d and e–h.
