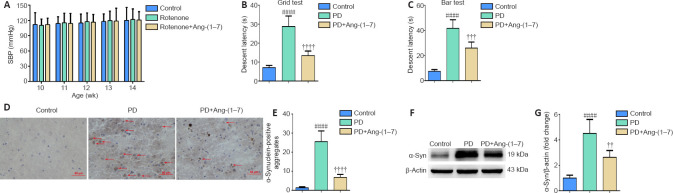
Figure 3.
Exogenous Ang-(1–7) infusion relieves characteristic parkinsonian behaviors and reduces the aggregation of α-synuclein in the substantia nigra in the rotenone-induced Parkinson's disease rat model.
(A) The SBP of rats was tracked by means of tail cuff, and differences were observed in the same group for different time points. Data are expressioned as mean ± SD (n = 6; two-way repeated measures analysis of variance). There was no significant difference in the SBP of rats between groups during the study (P > 0.05). (B) Descent latency of different groups in catalepsy tests was determined by agrid test. (C) Descent latency of different groups was determined by bar test. (D) The α-syn pathology in the SN of different groups was observed by immunohistochemical staining and fluorescent microscopy (original magnification, 400×). After incubation with primary and secondary antibodies, slides were stained with diaminobenzidine and counterstained with hematoxylin. The red arrows indicate α-syn-positive aggregates. (E) Quantitative results of α-syn-positive aggregates. (F) The α-syn expression in the SN in different groups was detected by Western blot assay. (G) Quantitative results of α-syn expression. Data are expressioned as the mean ± SD (B, C, E, G: n = 6, one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey's post hoc test). ####P < 0.0001, vs. control group; ††P < 0.01, †††P < 0.001, ††††P < 0.0001, vs. PD group. 1 mmHg = 0.133 kPa. Ang-(1–7): Angiotensin-(1–7); PD: Parkinson's disease; SBP: systolic blood pressure; SN: substantia nigra; w: weeks; α-syn: α-synuclein.