Figure 2.
NCAM1 mediates the clustering of neurites.
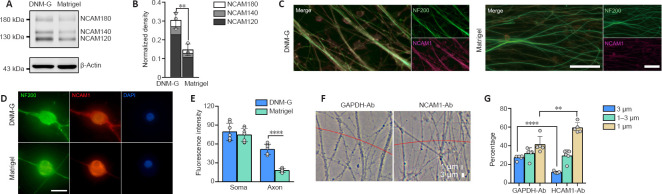
(A, B) Immunoblotting confirming the upregulation of all three NCAM1 isoforms (NCAM120, NCAM140, and NCAM180) in DNM-G-treated DRGs, compared with Matrigel-treated DRGs (n = 3 independent experiments, **P = 0.0063, Student's t-test). The expression of NCAM1 was normalized to β-actin. (C) Immunofluorescence images of NCAM1 (red, stained by Cy3) expression in axons (labeled with NF200, green, stained by Alexa Fluor 488). The NCAM1 signals in the DNM-G group were stronger than those in the Matrigel group. (D) Immunofluorescence images showing the lack of NCAM1 (red, stained by Cy3) in axons but not somas in the Matrigel group, compared with the DNM-G group. (E) Comparison of NCAM1 fluorescence intensity in DRG somas and axons between the DNM-G and Matrigel groups (n = 7 cultures, ****P < 0.0001, Student's t-test). (F) Phase contrast microscopy of single axons/axon bundles in DNM-G after antibody blocking for 48 hours. The red line indicates a 1-mm distance from the DRG tissue block center. We measured the diameter of each axon or bundle across the red line. (G) Distributions of axon bundle diameters after GAPDH-Ab and NCAM1-Ab treatments (n = 5 cultures, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001, Student's t-test). Scale bars: 50 μm in C and 8 μm in D. DNM-G: Decellularized nerve matrix-gel; DRG: dorsal root ganglion; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; NCAM1: neural cell adhesion molecule 1.