Figure 4.
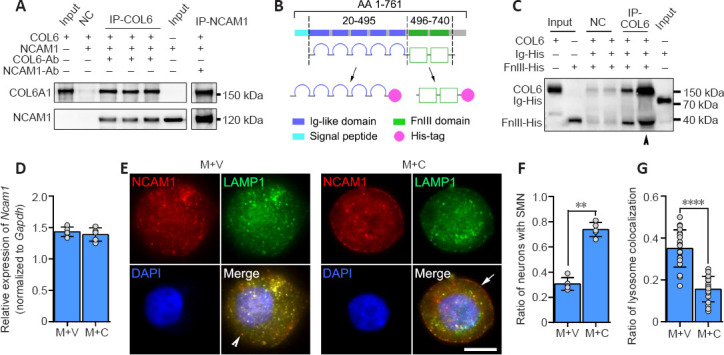
COL6-NCAM1 interaction inhibits lysosomal degradation of NCAM1.
(A) Co-immunoprecipitation revealed a direct interaction between COL6 and NCAM1 (isoform NCAM120). (B) Schematic diagram of recombinant protein domain construction. (C) Co-immunoprecipitation demonstrated that COL6 interacted with the NCAM1 FN3 domain but not the Ig-like domain. Arrowheads indicate five times the amount of proteins for the same assay. (D) qRT-PCR analyses of Ncam1 genes in DRGs growing on M + V and M + C substrates. Gapdh was used as the reference gene (n = 5 cultures, P = 0.4704, Student's t-test). (E) Representative fluorescence images of NCAM1 (red, stained by Cy3) and lysosomes (green, stained by lysosomes-GFP) in DRG somas. In the M + V group, the lysosomes were predominantly scattered in the cytoplasm (arrowhead indicates granular cytoplasmic NCAM1). In the M + C group, the lysosomes were mainly distributed on the membrane (arrow indicates smooth membrane NCAM1). (F) The ratio of neurons with SMN, compared between groups (n = 5 cultures, **P = 0.0079, Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney test). (G) The ratio of lysosome colocalization with NCAM1, manually counted, revealed a significant reduction in COL6-treated (M + C) DRGs compared with vehicle-treated (M + V) DRGs (n = 20 cells from three independent experiments, ****P < 0.0001, Student's t-test). Scale bar: 5 μm in E. COL6: Collagen VI; DRG: dorsal root ganglion; FN3: fibronectin type III domains; Gapdh: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; GFP: green fluorescent protein; M + V: Matrigel + Vehicle; M + C: Matrigel + COL6; NCAM1: neural cell adhesion molecule 1; qRT-PCR: real-time quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction; SMN: smooth membrane NCAM1.
