Figure 4.
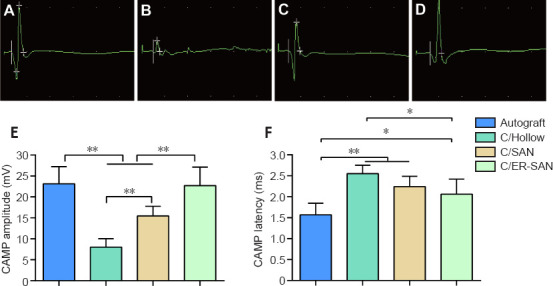
Chitin scaffold combined with autologous small nerve improves the electrophysiological assessment results in rats 12 weeks after inducing sciatic nerve defects.
(A–D) Representative images of the CAMP for the Autograft (A), C/Hollow (B), C/SAN (C), and C/SAN-ER (D) groups. (E) The mean CAMP amplitude for each group. (F) The mean CAMP latency for each group. Autograft group: the nerve gap bridged by the autograft; C/Hollow group: the nerve gap bridged by the hollow chitin conduit; C/SAN group: the nerve gap bridged by the chitin biological conduit in which a small nerve was inside; C/SAN-ER group: the nerve gap bridged by the chitin conduit in which a small nerve with its epineurium removed was inside. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 6). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (one-way analysis of variance followed by Student-Newman-Keuls test). CAMP: Complex muscle action potential.
