Figure 1.
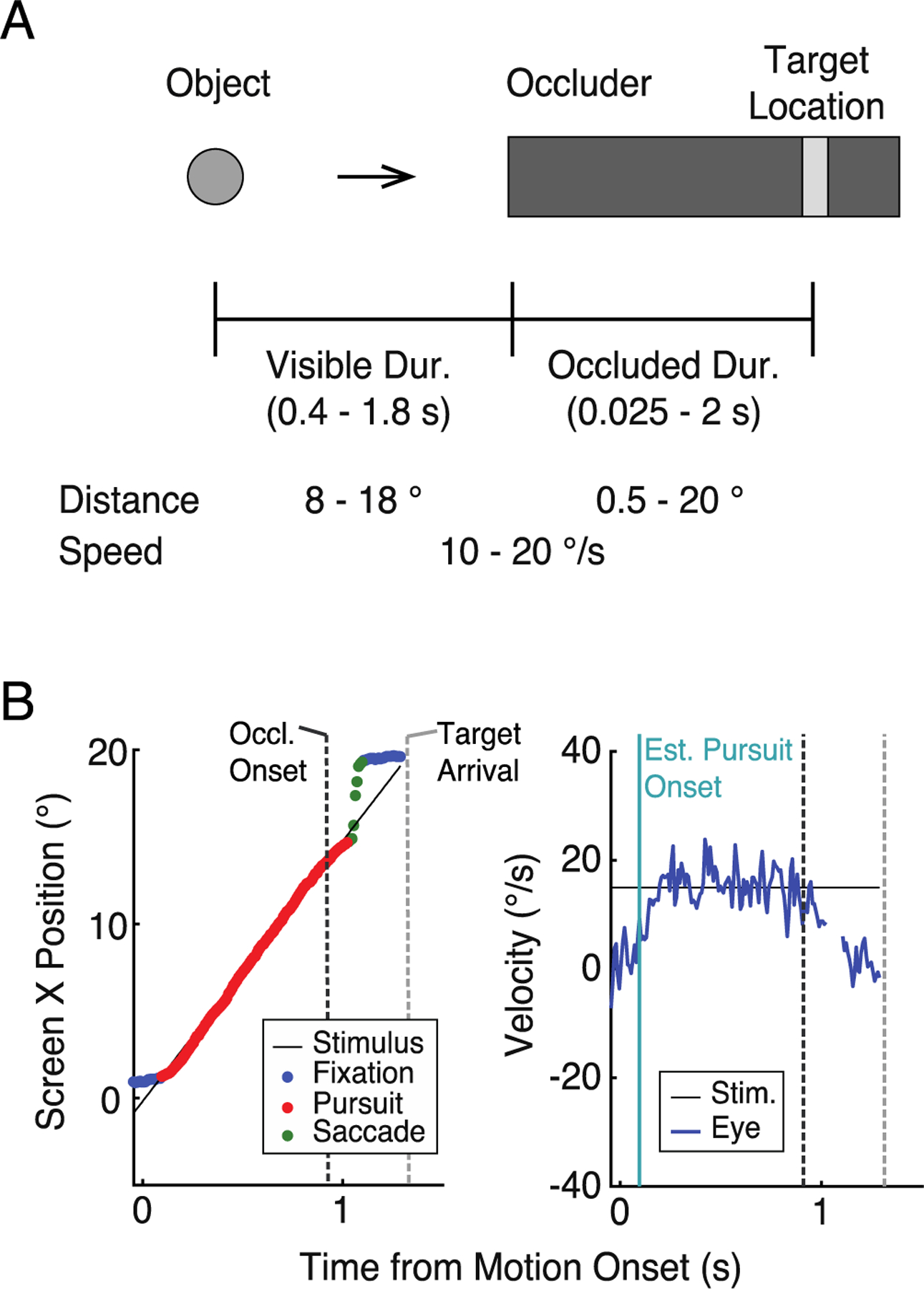
A: Schematic illustrations of experimental setting. The actual moving object was a bird from a popular smartphone game (Angry Birds; Rovio Entertainment, 2009), here depicted as a grey circle. The object moved for varying durations (visible duration) before it disappeared behind the occluder (darker grey bar). Participants responded when they thought that the object had arrived at the target location (lighter grey bar). The actual target arrival time (occluded duration) also varied from trial to trial. The visible and occluded durations were determined by sampling the distance and speed from uniform distributions (see Methods). B: An example eye movement trace from one participant. Darker and lighter vertical dashed lines indicate occluder onset and the actual target arrival time, respectively. Left: Horizontal eye position. Each dot is an eye movement sample with the color reflecting the classification based on our analysis (see Methods). Right: Eye velocity trace, with saccade removed.
