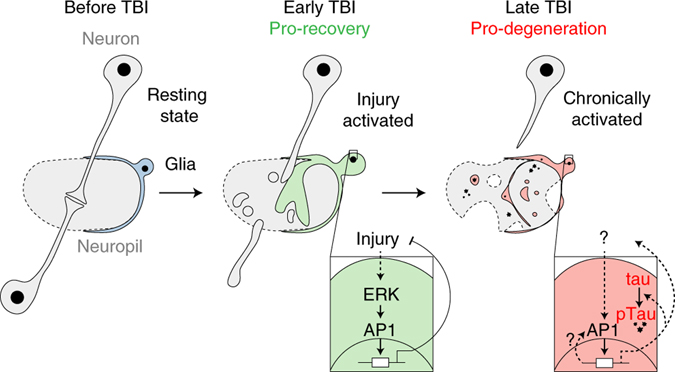
Fig. 7 |. Glial AP1 promotes early TBI recovery but chronically drives tauopathy.
Left, simplified fly brain schematic showing an intracortical synapse surrounded by a resting state glial cell. Middle, in the early post-injury period (<3 dpi), ERK activates glial AP1, which orchestrates a gene program vital to injury recovery. Right, sustained AP1 activity fosters a prodegenerative glial state that promotes human tau pathology. Solid lines are known interactions; dashed lines are proposed interactions.